Cynarine
|

|
| Names
|
Preferred IUPAC name
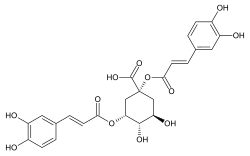
(1R,3R,4S,5R)-1,3-Bis{[(2E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxycyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid |
| Other names
1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid; Cynarin; Cinarin; Cinarine
|
| Identifiers
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ChEMBL
|
|
| ChemSpider
|
|
|
|
|
| UNII
|
|
|
|
|
InChI=1S/C25H24O12/c26-15-5-1-13(9-17(15)28)3-7-21(31)36-20-12-25(24(34)35,11-19(30)23(20)33)37-22(32)8-4-14-2-6-16(27)18(29)10-14/h1-10,19-20,23,26-30,33H,11-12H2,(H,34,35)/b7-3+,8-4+/t19-,20-,23+,25-/m1/s1  N NKey: YDDUMTOHNYZQPO-RVXRWRFUSA-N  N NInChI=1/C25H24O12/c26-15-5-1-13(9-17(15)28)3-7-21(31)36-20-12-25(24(34)35,11-19(30)23(20)33)37-22(32)8-4-14-2-6-16(27)18(29)10-14/h1-10,19-20,23,26-30,33H,11-12H2,(H,34,35)/b7-3+,8-4+/t19-,20-,23+,25-/m1/s1 Key: YDDUMTOHNYZQPO-RVXRWRFUBT
|
C1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](C[C@]1(C(=O)O)OC(=O)/C=C/C2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)OC(=O)/C=C/C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O)O)O
|
| Properties
|
|
|
C25H24O12
|
| Molar mass
|
516.455 g·mol−1
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references
|
Cynarine is a hydroxycinnamic acid derivative and a biologically active chemical constituent of artichoke (Cynara cardunculus).[1]
Chemically, it is an ester formed from quinic acid and two units of caffeic acid.
See also
References
|
|---|
| Aglycones | | Precursor | |
|---|
Monohydroxycinnamic acids
(Coumaric acids) | |
|---|
| Dihydroxycinnamic acids | |
|---|
| Trihydroxycinnamic acids | |
|---|
| O-methylated forms | |
|---|
| others | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Esters | | glycoside-likes | Esters of
caffeic acid
with cyclitols | |
|---|
| Glycosides | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Tartaric acid esters | |
|---|
Other esters
with caffeic acid | |
|---|
Caffeoyl phenylethanoid
glycoside (CPG) |
- Echinacoside
- Calceolarioside A, B, C, F
- Chiritoside A, B, C
- Cistanoside A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
- Conandroside
- Myconoside
- Pauoifloside
- Plantainoside A
- Plantamajoside
- Tubuloside B
- Verbascoside (Isoverbascoside, 2′-Acetylverbascoside)
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Oligomeric forms | | Dimers |
- Diferulic acids (DiFA) : 5,5′-Diferulic acid, 8-O-4′-Diferulic acid, 8,5′-Diferulic acid, 8,5′-DiFA (DC), 8,5′-DiFA (BF), 8,8′-Diferulic acid
|
|---|
| Trimers | |
|---|
| Tetramers | |
|---|
|
|---|
Conjugates with
coenzyme A (CoA) | |
|---|

