In probability and statistics , the skewed generalized "t" distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions . The distribution was first introduced by Panayiotis Theodossiou[ 1] [ 2] [ 3] [ 4] [ 5] [ 6] [ 7] [ 1] [ 5]
Definition
Probability density function
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
p
,
q
)
=
p
2
v
σ
q
1
p
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
[
1
+
|
x
−
μ
+
m
|
p
q
(
v
σ
)
p
(
1
+
λ
sgn
(
x
−
μ
+
m
)
)
p
]
1
p
+
q
{\displaystyle f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,p,q)={\frac {p}{2v\sigma q^{\frac {1}{p}}B({\frac {1}{p}},q)\left[1+{\frac {|x-\mu +m|^{p}}{q(v\sigma )^{p}(1+\lambda \operatorname {sgn}(x-\mu +m))^{p}}}\right]^{{\frac {1}{p}}+q}}}}
where
B
{\displaystyle B}
beta function ,
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
σ
>
0
{\displaystyle \sigma >0}
−
1
<
λ
<
1
{\displaystyle -1<\lambda <1}
p
>
0
{\displaystyle p>0}
q
>
0
{\displaystyle q>0}
kurtosis .
m
{\displaystyle m}
v
{\displaystyle v}
In the original parameterization[ 1]
m
=
λ
v
σ
2
q
1
p
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
{\displaystyle m=\lambda v\sigma {\frac {2q^{\frac {1}{p}}B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)}}}
and
v
=
q
−
1
p
(
1
+
3
λ
2
)
B
(
3
p
,
q
−
2
p
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
−
4
λ
2
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
2
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
2
{\displaystyle v={\frac {q^{-{\frac {1}{p}}}}{\sqrt {(1+3\lambda ^{2}){\frac {B({\frac {3}{p}},q-{\frac {2}{p}})}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)}}-4\lambda ^{2}{\frac {B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})^{2}}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)^{2}}}}}}}
These values for
m
{\displaystyle m}
v
{\displaystyle v}
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
p
q
>
1
{\displaystyle pq>1}
σ
2
{\displaystyle \sigma ^{2}}
p
q
>
2
{\displaystyle pq>2}
m
{\displaystyle m}
p
q
>
1
{\displaystyle pq>1}
v
{\displaystyle v}
p
q
>
2
{\displaystyle pq>2}
The parameterization that yields the simplest functional form of the probability density function sets
m
=
0
{\displaystyle m=0}
v
=
1
{\displaystyle v=1}
μ
+
2
v
σ
λ
q
1
p
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
{\displaystyle \mu +{\frac {2v\sigma \lambda q^{\frac {1}{p}}B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)}}}
and a variance of
σ
2
q
2
p
(
(
1
+
3
λ
2
)
B
(
3
p
,
q
−
2
p
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
−
4
λ
2
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
2
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
2
)
{\displaystyle \sigma ^{2}q^{\frac {2}{p}}((1+3\lambda ^{2}){\frac {B({\frac {3}{p}},q-{\frac {2}{p}})}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)}}-4\lambda ^{2}{\frac {B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})^{2}}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)^{2}}})}
The
λ
{\displaystyle \lambda }
M
{\displaystyle M}
∫
−
∞
M
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
p
,
q
)
d
x
=
1
−
λ
2
{\displaystyle \int _{-\infty }^{M}f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,p,q)\mathrm {d} x={\frac {1-\lambda }{2}}}
Since
−
1
<
λ
<
1
{\displaystyle -1<\lambda <1}
λ
{\displaystyle \lambda }
−
1
<
λ
<
0
{\displaystyle -1<\lambda <0}
0
<
λ
<
1
{\displaystyle 0<\lambda <1}
λ
=
0
{\displaystyle \lambda =0}
Finally,
p
{\displaystyle p}
q
{\displaystyle q}
p
{\displaystyle p}
q
{\displaystyle q}
[ 1]
p
{\displaystyle p}
q
{\displaystyle q}
Moments
Let
X
{\displaystyle X}
h
t
h
{\displaystyle h^{th}}
E
[
(
X
−
E
(
X
)
)
h
]
{\displaystyle E[(X-E(X))^{h}]}
p
q
>
h
{\displaystyle pq>h}
∑
r
=
0
h
(
h
r
)
(
(
1
+
λ
)
r
+
1
+
(
−
1
)
r
(
1
−
λ
)
r
+
1
)
(
−
λ
)
h
−
r
(
v
σ
)
h
q
h
p
B
(
r
+
1
p
,
q
−
r
p
)
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
h
−
r
2
r
−
h
+
1
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
h
−
r
+
1
{\displaystyle \sum _{r=0}^{h}{\binom {h}{r}}((1+\lambda )^{r+1}+(-1)^{r}(1-\lambda )^{r+1})(-\lambda )^{h-r}{\frac {(v\sigma )^{h}q^{\frac {h}{p}}B({\frac {r+1}{p}},q-{\frac {r}{p}})B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})^{h-r}}{2^{r-h+1}B({\frac {1}{p}},q)^{h-r+1}}}}
The mean, for
p
q
>
1
{\displaystyle pq>1}
μ
+
2
v
σ
λ
q
1
p
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
−
m
{\displaystyle \mu +{\frac {2v\sigma \lambda q^{\frac {1}{p}}B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)}}-m}
The variance (i.e.
E
[
(
X
−
E
(
X
)
)
2
]
{\displaystyle E[(X-E(X))^{2}]}
p
q
>
2
{\displaystyle pq>2}
(
v
σ
)
2
q
2
p
(
(
1
+
3
λ
2
)
B
(
3
p
,
q
−
2
p
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
−
4
λ
2
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
2
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
2
)
{\displaystyle (v\sigma )^{2}q^{\frac {2}{p}}((1+3\lambda ^{2}){\frac {B({\frac {3}{p}},q-{\frac {2}{p}})}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)}}-4\lambda ^{2}{\frac {B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})^{2}}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)^{2}}})}
The skewness (i.e.
E
[
(
X
−
E
(
X
)
)
3
]
{\displaystyle E[(X-E(X))^{3}]}
p
q
>
3
{\displaystyle pq>3}
2
q
3
/
p
λ
(
v
σ
)
3
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
3
(
8
λ
2
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
3
−
3
(
1
+
3
λ
2
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
{\displaystyle {\frac {2q^{3/p}\lambda (v\sigma )^{3}}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)^{3}}}{\Bigg (}8\lambda ^{2}B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})^{3}-3(1+3\lambda ^{2})B({\frac {1}{p}},q)}
×
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
B
(
3
p
,
q
−
2
p
)
+
2
(
1
+
λ
2
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
2
B
(
4
p
,
q
−
3
p
)
)
{\displaystyle \times B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})B({\frac {3}{p}},q-{\frac {2}{p}})+2(1+\lambda ^{2})B({\frac {1}{p}},q)^{2}B({\frac {4}{p}},q-{\frac {3}{p}}){\Bigg )}}
The kurtosis (i.e.
E
[
(
X
−
E
(
X
)
)
4
]
{\displaystyle E[(X-E(X))^{4}]}
p
q
>
4
{\displaystyle pq>4}
q
4
/
p
(
v
σ
)
4
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
4
(
−
48
λ
4
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
4
+
24
λ
2
(
1
+
3
λ
2
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
2
{\displaystyle {\frac {q^{4/p}(v\sigma )^{4}}{B({\frac {1}{p}},q)^{4}}}{\Bigg (}-48\lambda ^{4}B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})^{4}+24\lambda ^{2}(1+3\lambda ^{2})B({\frac {1}{p}},q)B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})^{2}}
×
B
(
3
p
,
q
−
2
p
)
−
32
λ
2
(
1
+
λ
2
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
2
B
(
2
p
,
q
−
1
p
)
B
(
4
p
,
q
−
3
p
)
{\displaystyle \times B({\frac {3}{p}},q-{\frac {2}{p}})-32\lambda ^{2}(1+\lambda ^{2})B({\frac {1}{p}},q)^{2}B({\frac {2}{p}},q-{\frac {1}{p}})B({\frac {4}{p}},q-{\frac {3}{p}})}
+
(
1
+
10
λ
2
+
5
λ
4
)
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
3
B
(
5
p
,
q
−
4
p
)
)
{\displaystyle +(1+10\lambda ^{2}+5\lambda ^{4})B({\frac {1}{p}},q)^{3}B({\frac {5}{p}},q-{\frac {4}{p}}){\Bigg )}}
Special Cases
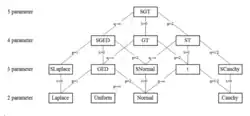
Special and limiting cases of the skewed generalized t distribution include the skewed generalized error distribution, the generalized t distribution introduced by McDonald and Newey,[ 6] [ 8] generalized normal distribution ), a skewed normal distribution, the student t distribution , the skewed Cauchy distribution, the Laplace distribution , the uniform distribution , the normal distribution , and the Cauchy distribution . The graphic below, adapted from Hansen, McDonald, and Newey,[ 2]
The skewed generalized t distribution tree
Skewed generalized error distribution
The Skewed Generalized Error Distribution (SGED) has the pdf:
lim
q
→
∞
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
p
,
q
)
{\displaystyle \lim _{q\to \infty }f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,p,q)}
=
f
SGED
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
p
)
=
p
2
v
σ
Γ
(
1
p
)
e
−
(
|
x
−
μ
+
m
|
v
σ
[
1
+
λ
sgn
(
x
−
μ
+
m
)
]
)
p
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{SGED}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,p)={\frac {p}{2v\sigma \Gamma ({\frac {1}{p}})}}e^{-\left({\frac {|x-\mu +m|}{v\sigma [1+\lambda \operatorname {sgn}(x-\mu +m)]}}\right)^{p}}}
where
m
=
λ
v
σ
2
2
p
Γ
(
1
2
+
1
p
)
π
{\displaystyle m=\lambda v\sigma {\frac {2^{\frac {2}{p}}\Gamma ({\frac {1}{2}}+{\frac {1}{p}})}{\sqrt {\pi }}}}
gives a mean of
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
v
=
π
Γ
(
1
p
)
π
(
1
+
3
λ
2
)
Γ
(
3
p
)
−
16
1
p
λ
2
Γ
(
1
2
+
1
p
)
2
Γ
(
1
p
)
{\displaystyle v={\sqrt {\frac {\pi \Gamma ({\frac {1}{p}})}{\pi (1+3\lambda ^{2})\Gamma ({\frac {3}{p}})-16^{\frac {1}{p}}\lambda ^{2}\Gamma ({\frac {1}{2}}+{\frac {1}{p}})^{2}\Gamma ({\frac {1}{p}})}}}}
gives a variance of
σ
2
{\displaystyle \sigma ^{2}}
Generalized t -distribution
The generalized t -distribution (GT) has the pdf:
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
=
0
,
p
,
q
)
{\displaystyle f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda {=}0,p,q)}
=
f
GT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
p
,
q
)
=
p
2
v
σ
q
1
p
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
[
1
+
|
x
−
μ
|
p
q
(
v
σ
)
p
]
1
p
+
q
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{GT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,p,q)={\frac {p}{2v\sigma q^{\frac {1}{p}}B({\frac {1}{p}},q)\left[1+{\frac {\left|x-\mu \right|^{p}}{q(v\sigma )^{p}}}\right]^{{\frac {1}{p}}+q}}}}
where
v
=
1
q
1
p
B
(
1
p
,
q
)
B
(
3
p
,
q
−
2
p
)
{\displaystyle v={\frac {1}{q^{\frac {1}{p}}}}{\sqrt {\frac {B({\frac {1}{p}},q)}{B({\frac {3}{p}},q-{\frac {2}{p}})}}}}
gives a variance of
σ
2
{\displaystyle \sigma ^{2}}
Skewed t -distribution
The skewed t -distribution (ST) has the pdf:
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
p
=
2
,
q
)
{\displaystyle f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,p{=}2,q)}
=
f
ST
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
q
)
=
Γ
(
1
2
+
q
)
v
σ
(
π
q
)
1
2
Γ
(
q
)
[
1
+
|
x
−
μ
+
m
|
2
q
(
v
σ
)
2
(
1
+
λ
sgn
(
x
−
μ
+
m
)
)
2
]
1
2
+
q
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{ST}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,q)={\frac {\Gamma ({\frac {1}{2}}+q)}{v\sigma (\pi q)^{\frac {1}{2}}\Gamma (q)\left[1+{\frac {\left|x-\mu +m\right|^{2}}{q(v\sigma )^{2}(1+\lambda \operatorname {sgn}(x-\mu +m))^{2}}}\right]^{{\frac {1}{2}}+q}}}}
where
m
=
λ
v
σ
2
q
1
2
Γ
(
q
−
1
2
)
π
1
2
Γ
(
q
)
{\displaystyle m=\lambda v\sigma {\frac {2q^{\frac {1}{2}}\Gamma (q-{\frac {1}{2}})}{\pi ^{\frac {1}{2}}\Gamma (q)}}}
gives a mean of
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
v
=
1
q
1
2
(
1
+
3
λ
2
)
1
2
q
−
2
−
4
λ
2
π
(
Γ
(
q
−
1
2
)
Γ
(
q
)
)
2
{\displaystyle v={\frac {1}{q^{\frac {1}{2}}{\sqrt {(1+3\lambda ^{2}){\frac {1}{2q-2}}-{\frac {4\lambda ^{2}}{\pi }}\left({\frac {\Gamma (q-{\frac {1}{2}})}{\Gamma (q)}}\right)^{2}}}}}}
gives a variance of
σ
2
{\displaystyle \sigma ^{2}}
Skewed Laplace distribution
The skewed Laplace distribution (SLaplace) has the pdf:
lim
q
→
∞
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
p
=
1
,
q
)
{\displaystyle \lim _{q\to \infty }f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,p{=}1,q)}
=
f
SLaplace
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
)
=
1
2
v
σ
e
−
|
x
−
μ
+
m
|
v
σ
(
1
+
λ
sgn
(
x
−
μ
+
m
)
)
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{SLaplace}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda )={\frac {1}{2v\sigma }}e^{-{\frac {|x-\mu +m|}{v\sigma (1+\lambda \operatorname {sgn}(x-\mu +m))}}}}
where
m
=
2
v
σ
λ
{\displaystyle m=2v\sigma \lambda }
gives a mean of
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
v
=
[
2
(
1
+
λ
2
)
]
−
1
2
{\displaystyle v=[2(1+\lambda ^{2})]^{-{\frac {1}{2}}}}
gives a variance of
σ
2
{\displaystyle \sigma ^{2}}
Generalized error distribution
The generalized error distribution (GED, also known as the generalized normal distribution ) has the pdf:
lim
q
→
∞
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
=
0
,
p
,
q
)
{\displaystyle \lim _{q\to \infty }f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda {=}0,p,q)}
=
f
GED
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
p
)
=
p
2
v
σ
Γ
(
1
p
)
e
−
(
|
x
−
μ
|
v
σ
)
p
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{GED}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,p)={\frac {p}{2v\sigma \Gamma ({\frac {1}{p}})}}e^{-\left({\frac {|x-\mu |}{v\sigma }}\right)^{p}}}
where
v
=
Γ
(
1
p
)
Γ
(
3
p
)
{\displaystyle v={\sqrt {\frac {\Gamma ({\frac {1}{p}})}{\Gamma ({\frac {3}{p}})}}}}
gives a variance of
σ
2
{\displaystyle \sigma ^{2}}
Skewed normal distribution
The skewed normal distribution (SNormal) has the pdf:
lim
q
→
∞
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
p
=
2
,
q
)
{\displaystyle \lim _{q\to \infty }f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,p{=}2,q)}
=
f
SNormal
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
)
=
1
v
σ
π
e
−
[
|
x
−
μ
+
m
|
v
σ
(
1
+
λ
sgn
(
x
−
μ
+
m
)
)
]
2
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{SNormal}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda )={\frac {1}{v\sigma {\sqrt {\pi }}}}e^{-\left[{\frac {|x-\mu +m|}{v\sigma (1+\lambda \operatorname {sgn}(x-\mu +m))}}\right]^{2}}}
where
m
=
λ
v
σ
2
π
{\displaystyle m=\lambda v\sigma {\frac {2}{\sqrt {\pi }}}}
gives a mean of
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
v
=
2
π
π
−
8
λ
2
+
3
π
λ
2
{\displaystyle v={\sqrt {\frac {2\pi }{\pi -8\lambda ^{2}+3\pi \lambda ^{2}}}}}
gives a variance of
σ
2
{\displaystyle \sigma ^{2}}
The distribution should not be confused with the skew normal distribution or another asymmetric version . Indeed, the distribution here is a special case of a bi-Gaussian, whose left and right widths are proportional to
1
−
λ
{\displaystyle 1-\lambda }
1
+
λ
{\displaystyle 1+\lambda }
t -distributionThe Student's t-distribution (T) has the pdf:
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
=
0
,
σ
=
1
,
λ
=
0
,
p
=
2
,
q
=
d
2
)
{\displaystyle f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu {=}0,\sigma {=}1,\lambda {=}0,p{=}2,q{=}{\tfrac {d}{2}})}
=
f
T
(
x
;
d
)
=
Γ
(
d
+
1
2
)
(
π
d
)
1
2
Γ
(
d
2
)
(
1
+
x
2
d
)
−
d
+
1
2
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{T}}(x;d)={\frac {\Gamma ({\frac {d+1}{2}})}{(\pi d)^{\frac {1}{2}}\Gamma ({\frac {d}{2}})}}\left(1+{\frac {x^{2}}{d}}\right)^{-{\frac {d+1}{2}}}}
v
=
2
{\displaystyle v={\sqrt {2}}}
Skewed Cauchy distribution
The skewed cauchy distribution (SCauchy) has the pdf:
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
p
=
2
,
q
=
1
2
)
{\displaystyle f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,p{=}2,q{=}{\tfrac {1}{2}})}
=
f
SCauchy
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
)
=
1
σ
π
[
1
+
|
x
−
μ
|
2
σ
2
(
1
+
λ
sgn
(
x
−
μ
)
)
2
]
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{SCauchy}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda )={\frac {1}{\sigma \pi \left[1+{\frac {\left|x-\mu \right|^{2}}{\sigma ^{2}(1+\lambda \operatorname {sgn}(x-\mu ))^{2}}}\right]}}}
v
=
2
{\displaystyle v={\sqrt {2}}}
m
=
0
{\displaystyle m=0}
The mean, variance, skewness, and kurtosis of the skewed Cauchy distribution are all undefined.
Laplace distribution
The Laplace distribution has the pdf:
lim
q
→
∞
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
=
0
,
p
=
1
,
q
)
{\displaystyle \lim _{q\to \infty }f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda {=}0,p{=}1,q)}
=
f
Laplace
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
)
=
1
2
σ
e
−
|
x
−
μ
|
σ
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{Laplace}}(x;\mu ,\sigma )={\frac {1}{2\sigma }}e^{-{\frac {|x-\mu |}{\sigma }}}}
v
=
1
{\displaystyle v=1}
The uniform distribution has the pdf:
lim
p
→
∞
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
,
p
,
q
)
{\displaystyle \lim _{p\to \infty }f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda ,p,q)}
=
f
(
x
)
=
{
1
2
v
σ
|
x
−
μ
|
<
v
σ
0
o
t
h
e
r
w
i
s
e
{\displaystyle =f(x)={\begin{cases}{\frac {1}{2v\sigma }}&|x-\mu |<v\sigma \\0&\mathrm {otherwise} \end{cases}}}
Thus the standard uniform parameterization is obtained if
μ
=
a
+
b
2
{\displaystyle \mu ={\frac {a+b}{2}}}
v
=
1
{\displaystyle v=1}
σ
=
b
−
a
2
{\displaystyle \sigma ={\frac {b-a}{2}}}
Normal distribution
The normal distribution has the pdf:
lim
q
→
∞
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
=
0
,
p
=
2
,
q
)
{\displaystyle \lim _{q\to \infty }f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda {=}0,p{=}2,q)}
=
f
Normal
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
)
=
e
−
(
|
x
−
μ
|
v
σ
)
2
v
σ
π
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{Normal}}(x;\mu ,\sigma )={\frac {e^{-\left({\frac {|x-\mu |}{v\sigma }}\right)^{2}}}{v\sigma {\sqrt {\pi }}}}}
where
v
=
2
{\displaystyle v={\sqrt {2}}}
gives a variance of
σ
2
{\displaystyle \sigma ^{2}}
Cauchy Distribution
The Cauchy distribution has the pdf:
f
SGT
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
,
λ
=
0
,
p
=
2
,
q
=
1
2
)
{\displaystyle f_{\text{SGT}}(x;\mu ,\sigma ,\lambda {=}0,p{=}2,q{=}{\tfrac {1}{2}})}
=
f
Cauchy
(
x
;
μ
,
σ
)
=
1
σ
π
[
1
+
(
x
−
μ
σ
)
2
]
{\displaystyle =f_{\text{Cauchy}}(x;\mu ,\sigma )={\frac {1}{\sigma \pi \left[1+\left({\frac {x-\mu }{\sigma }}\right)^{2}\right]}}}
v
=
2
{\displaystyle v={\sqrt {2}}}
References
Hansen, B. (1994). "Autoregressive Conditional Density Estimation". International Economic Review 35 (3): 705– 730. doi :10.2307/2527081 . JSTOR 2527081 . Hansen, C.; McDonald, J.; Newey, W. (2010). "Instrumental Variables Estimation with Flexible Distributions". Journal of Business and Economic Statistics 28 : 13– 25. doi :10.1198/jbes.2009.06161 . hdl :10419/79273 S2CID 11370711 . Hansen, C.; McDonald, J.; Theodossiou, P. (2007). "Some Flexible Parametric Models for Partially Adaptive Estimators of Econometric Models" . Economics: The Open-Access, Open-Assessment e-Journal . 1 (2007– 7): 1. doi :10.5018/economics-ejournal.ja.2007-7 hdl :20.500.14279/1024 McDonald, J.; Michefelder, R.; Theodossiou, P. (2009). "Evaluation of Robust Regression Estimation Methods and Intercept Bias: A Capital Asset Pricing Model Application" (PDF) . Multinational Finance Journal . 15 (3/4): 293– 321. doi :10.17578/13-3/4-6 . S2CID 15012865 . McDonald, J.; Michelfelder, R.; Theodossiou, P. (2010). "Robust Estimation with Flexible Parametric Distributions: Estimation of Utility Stock Betas". Quantitative Finance . 10 (4): 375– 387. doi :10.1080/14697680902814241 . S2CID 11130911 . McDonald, J.; Newey, W. (1988). "Partially Adaptive Estimation of Regression Models via the Generalized t Distribution". Econometric Theory 4 (3): 428– 457. doi :10.1017/s0266466600013384 . S2CID 120305707 . Savva, C.; Theodossiou, P. (2015). "Skewness and the Relation between Risk and Return". Management Science Theodossiou, P. (1998). "Financial Data and the Skewed Generalized T Distribution". Management Science 44 (12–part–1): 1650– 1661. doi :10.1287/mnsc.44.12.1650 .
External links
Notes
^ a b c d Theodossiou, P (1998). "Financial Data and the Skewed Generalized T Distribution". Management Science . 44 (12–part–1): 1650– 1661. doi :10.1287/mnsc.44.12.1650 . ^ a b Hansen, C.; McDonald, J.; Newey, W. (2010). "Instrumental Variables Estimation with Flexible Distributions". Journal of Business and Economic Statistics . 28 : 13– 25. doi :10.1198/jbes.2009.06161 . hdl :10419/79273 S2CID 11370711 . ^ Hansen, C., J. McDonald, and P. Theodossiou (2007) "Some Flexible Parametric Models for Partially Adaptive Estimators of Econometric Models" Economics: The Open-Access, Open-Assessment E-Journal
^ McDonald, J.; Michelfelder, R.; Theodossiou, P. (2009). "Evaluation of Robust Regression Estimation Methods and Intercept Bias: A Capital Asset Pricing Model Application" (PDF) . Multinational Finance Journal . 15 (3/4): 293– 321. doi :10.17578/13-3/4-6 . S2CID 15012865 . ^ a b McDonald J., R. Michelfelder, and P. Theodossiou (2010) "Robust Estimation with Flexible Parametric Distributions: Estimation of Utility Stock Betas" Quantitative Finance 375-387.
^ a b McDonald, J.; Newey, W. (1998). "Partially Adaptive Estimation of Regression Models via the Generalized t Distribution". Econometric Theory . 4 (3): 428– 457. doi :10.1017/S0266466600013384 . S2CID 120305707 . ^ Savva C. and P. Theodossiou (2015) "Skewness and the Relation between Risk and Return" Management Science , forthcoming.
^ Hansen, B (1994). "Autoregressive Conditional Density Estimation". International Economic Review . 35 (3): 705– 730. doi :10.2307/2527081 . JSTOR 2527081 .
Discrete
with finite with infinite
Continuous
supported on a supported on a supported with support
Mixed
Multivariate Directional Degenerate singular Families