Violence and Harassment Convention
| Convention concerning the elimination of violence and harassment in the world of work | |
|---|---|
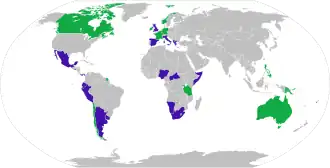 Convention in force
Ratifiers (Convention not yet in force) | |
| Signed | 21 June 2019 |
| Location | Geneva |
| Effective | 25 June 2021[1] |
| Condition | 22 ratifications |
| Parties | 27[1] |
| Ratifiers | 39[1] |
| Depositary | Director-General of the International Labour Office |
| Languages | French and English |
The Violence and Harassment Convention, formally the Convention concerning the elimination of violence and harassment in the world of work is a convention to "recognize the right of everyone to a world of work free from violence and harassment, including gender-based violence and harassment".[2] It is the 190th ILO convention (code C190) and was adopted during the 108th session of the International Labour Organization.[3]
Ratifications
The convention entered into force on 25 June 2021, upon ratification of Fiji and Uruguay.[1] Twenty-one other countries have deposited their instrument of ratification, but the convention only enters into force 1 year after ratification. As of 2024, the convention had been ratified by 39 states.
| Country | Date | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 6 May 2022 | In force | |
| 9 May 2022 | In force | |
| 23 February 2021 | In force | |
| 9 June 2023 | Will enter into force on 9 June 2024 | |
| 30 November 2022 | In force | |
| 1 September 2022 | In force | |
| 13 June 2023 | Will enter into force on 13 June 2024 | |
| 30 January 2023 | In force | |
| 9 June 2022 | In force | |
| 12 June 2023 | Will enter into force on 12 June 2024 | |
| 19 May 2021 | In force | |
| 7 June 2022 | In force | |
| 25 June 2020 | In force | |
| 12 April 2023 | In force | |
| 14 June 2023 | Will enter into force on 14 June 2024 | |
| 30 Aug 2021 | In force | |
| 12 January 2023 | In force | |
| 29 October 2021 | In force | |
| 15 March 2023 | In force | |
| 1 July 2021 | In force | |
| 6 July 2022 | In force | |
| 9 December 2020 | In force | |
| 8 November 2022 | In force | |
| 20 October 2023 | Will enter into force on 20 October 2024 | |
| 6 October 2023 | Will enter into force on 6 October 2024 | |
| 1 November 2022 | In force | |
| 27 September 2023 | Will enter into force on 27 September 2024 | |
| 8 June 2022 | In force | |
| 20 February 2024 | Will enter into force on 20 February 2025 | |
| 16 February 2024 | Will enter into force on 16 February 2025 | |
| 19 March 2024 | Will enter into force on 19 March 2025 | |
| 1 November 2023 | Will enter into force on 1 November 2024 | |
| 14 April 2022 | In force | |
| 8 March 2021 | In force | |
| 29 November 2021 | In force | |
| 25 May 2022 | In force | |
| 7 August 2023 | Will enter into force on 7 August 2024 | |
| 7 March 2022 | In force | |
| 12 June 2020 | In force |
References
- ^ a b c d "Ratifications of C190 - Violence and Harassment Convention, 2019 (No. 190)". ILO. Retrieved 29 December 2023.
- ^ "Eliminating Violence and Harassment in the World of Work". ILO. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ "C190 - Violence and Harassment Convention, 2019 (No. 190)". ILO. Retrieved 2 August 2021.