1789 United States House of Representatives elections in Georgia|
|
|
|
|
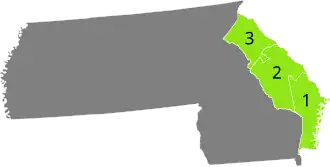 Anti-Administration gain Undistricted territory |
Congressional elections to the 1st United States Congress were held in Georgia on February 9, 1789, for the state's three congressional districts.[1] All elected representatives were members of the Anti-Administration political faction in Congress.[2]
The Georgia Election Act of 1789 established a mixed at-large/district system for congressional elections. Under the act, representatives were elected at-large on a general ticket but for three district-based seats, for which candidates were required to be residents. Each voter was allowed to cast three votes, one for a candidate in each district. Some candidates received votes in multiple districts.[1][3]
The election returns were opened on February 26. Only the returns of Richmond, Wilkes, Effingham, Chatham, Liberty, Burke, and Washington Counties were counted, as they had been received in time. The returns from Greene, Glynn, and Camden Counties came in too late but were published anyways. All elected representatives would've won with the returns of those counties included.[1]
Lower District
1789 Georgia's Lower congressional district election|
|
|
|
 Jackson: 40–50% 60–70% 80–90% >90%
Houstoun: 70-80%
Osborne: 50-60% 80-90%
No vote/data Non-County area |
|
The Lower District was also known as the Eastern District or the First District.[3] Jackson led a Savannah-based political faction, referred to as the Jackson party, centered in Coastal Georgia.[4]
Middle District
1789 Georgia's Middle congressional district election|
|
|
|
 Baldwin: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% >90%
Houstoun: 70-80%
Sumner: 50-60%
No vote/data Non-County area |
|
The Middle District was also known as the Center District or the Second District.[3]
Upper District
1789 Georgia's Upper congressional district election|
|
|
|
 Mathews: >90%
Osborne: >90%
No vote/data Non-County area |
|
The Upper District was also known as the Western District or the Third District.[3]
See also
References
|
|---|
U.S.
President | |
|---|
U.S.
Senate | |
|---|
U.S.
House | |
|---|
States and
territories |
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Georgia
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New York
- North Carolina
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- Virginia
|
|---|
|
|---|
Elections spanning
two years
(through 1879) | |
|---|
Elections held
in a single year
(starting 1880) | Regulars
and
even-year
specials | |
|---|
Odd-year
specials | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Elections by state |
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
|
|---|
| Seat ratings | |
|---|
| Speaker elections | |
|---|
| Summaries | |
|---|
- Senate elections
- Presidential elections
- Gubernatorial elections
|