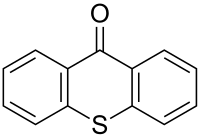
Thioxanthone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
9H-Thioxanthen-9-one | |
| Other names
Thioxanthenone; 9-Oxothioxanthene; Thioxanthen-9-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.046 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H8OS | |
| Molar mass | 212.27 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Pale yellow solid[1] |
| Melting point | 211 °C (412 °F; 484 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 273 °C (523 °F; 546 K)[2] (940 hPa) |
| Nearly insoluble | |
| Solubility in sulfuric acid | Soluble[2] |
| −130·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Thioxanthone is a heterocyclic compound that is a sulfur analog of xanthone.
Thioxanthone can be prepared by the reaction of diphenyl sulfide with phosgene in the presence of catalytic aluminium chloride.[2] This synthesis can be seen as a special case of the Friedel-Crafts acylation. The reduction product is thioxanthene.
Thioxanthone dissolves in concentrated sulfuric acid to give a yellow colored liquid with intense green fluorescence. A mixture of the thioxanthone derivatives of 2- and 4-isopropylthioxanthone (ITX) is used in the printing industry. Pharmaceutical drugs that are derivatives of thioxanthone include hycanthone and lucanthone.
References
- ^ Thioxanthone at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ a b c d Merck Index, 14th Edition, 1610
External links
 Media related to thioxanthones at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to thioxanthones at Wikimedia Commons