Splenius cervicis muscle
| Splenius cervicis muscle | |
|---|---|
 Muscles connecting the upper extremity to the vertebral column. (Splenius capitis et cervicis labeled at upper right, at neck.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Spinous processes of T3-T6 |
| Insertion | Transverse processes of C1-C3 |
| Artery | Transverse cervical artery and occipital artery |
| Nerve | Posterior rami of the lower Cervical spinal nerves |
| Actions | Bilaterally: Extend the head and neck, Unilaterally: Lateral flexion to the same side, Rotation to the same side. |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus splenius cervicis |
| TA98 | A04.3.02.104 |
| TA2 | 2274 |
| FMA | 22681 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The splenius cervicis (/ˈspliːniəs sərˈvaɪsɪs/) (also known as the splenius colli, /- ˈkɒlaɪ/) is a muscle in the back of the neck. It arises by a narrow tendinous band from the spinous processes of the third to the sixth thoracic vertebrae; it is inserted, by tendinous fasciculi, into the posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the upper two or three cervical vertebrae.
Its name is based on the Greek word σπληνίον, splenion (meaning a bandage) and the Latin word cervix (meaning a neck).[1] The word collum also refers to the neck in Latin.[1]
The function of the splenius cervicis muscle is extension of the cervical spine, rotation to the ipsilateral side and lateral flexion to the ipsilateral side.[2]
Additional images
-
 Position of splenius cervicis muscle (shown in red).
Position of splenius cervicis muscle (shown in red). -
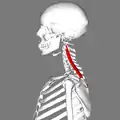 Lateral view.
Lateral view. -
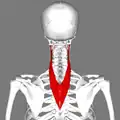 Posterior view.
Posterior view. -
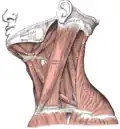 Muscles of the neck. Lateral view.
Muscles of the neck. Lateral view. -
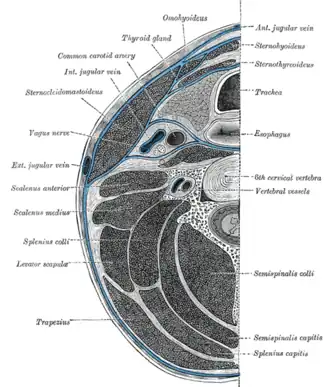 Section of the neck at the level of the sixth cervical vertebra.
Section of the neck at the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. -
 Splenius and Semispinalis
Splenius and Semispinalis -
 Splenius
Splenius
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 397 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 397 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b Arnold, MA; Bryce, Deborah. "Arnold's Glossary of Anatomy". The University of Sydney.
- ^ R.T. Floyd, Manual of Structural Kinesiology, 2012, 18th Ed.
External links