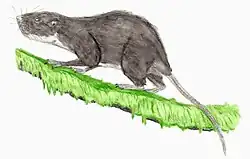
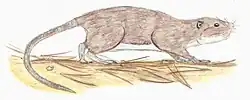
Archboldomys
| Archboldomys | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Muridae |
| Tribe: | Hydromyini |
| Genus: | Musser, 1982 |
| Species | |
Archboldomys, the shrew-mice, are a genus of rodents in the family Muridae. They are carnivores that feed on invertebrates much like shrews do. An apparently smaller relatives of the true shrew-rats Chrotomys and Rhynchomys, Archboldomys are somewhat convergent to the more distantly related Crunomys.[1]
The species are:
- Mount Isarog shrew-mouse, Archboldomys luzonensis[2]
- Large Cordillera shrew-mouse, Archboldomys maximus[1]
References
- Balete, Danilo S.; Rickart, Eric A. & Heaney, Lawrence R. (2006): A new species of the shrew-mouse, Archboldomys (Rodentia: Muridae: Murinae), from the Philippines. Systematics and Biodiversity 4(4): 489–501. doi:10.1017/S1477200006002003 (HTML abstract)
- Musser, G.G. & Carleton, M.D. (2005): Superfamily Muroidea. In: Wilson, D.E. & Reeder, D.M. (eds.): Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference: 894–1531. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore.
- Musser, G.G. (1982): Results of the Archbold Expeditions. No. 110. Crunomys and the small-bodied shrew rats native to the Philippine Islands and Sulawesi (Celebes). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 174(1): 1-95.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Archboldomys | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Additional terms may apply for the media files.