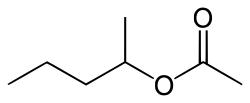
sec-Amyl acetate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentan-2-yl acetate | |
| Other names
1-Methylbutyl acetate
2-Pentanol acetate 2-Pentyl ester of acetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.952 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 130.187 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Mild,[1] like bananas[2] |
| Density | 0.87 g/mL (20°C)[1] |
| Melting point | −78 °C; −109 °F; 195 K[1] |
| Boiling point | 121 °C; 249 °F; 394 K[1] |
| 0.2g/100g water (20°C)[2] | |
| Vapor pressure | 7 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Warning[2] | |
| H226[2] | |
| Flash point | 32 °C; 89 °F; 305 K[1] |
| 380 °C (716 °F; 653 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1–7.5% (20°C)[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LCLo (lowest published)
|
9200 ppm (guinea pig, 7 hr) 10,000 ppm (guinea pig, 5 hr)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 125 ppm (650 mg/m3)[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 125 ppm (650 mg/m3)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1000 ppm[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
sec-Amyl acetate is an organic compound and an ester. It is formed in an esterification reaction of sec-amyl alcohol (2-pentanol) and acetic acid.[2] It is a colorless liquid.
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0032". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b c d e "2-Pentyl Acetate". PubChem. NCBI. Archived from the original on October 11, 2015.
- ^ "sec-Amyl acetate". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).