Pinacyanol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
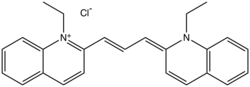
(2E)-1-ethyl-2-[(E)-3-(1-ethylquinolin-1-ium-2-yl)prop-2-enylidene]quinoline;chloride
| |
| Other names
Quinaldine blue
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.182 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H25ClN2 | |
| Molar mass | 388.94 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | blue solid |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Pinacyanol is a cyanine dye. It is an organic cation, typically isolated as the chloride or iodide salts. The blue dye is prepared from 2-methylquinoline by quaternization with ethyl chloride or ethyl iodide. Condensation with formaldehyde results in coupling. Subsequent oxidation of the leuco intermediate gives the dye.[1] Pinacyanol is a prototypical cyanine dye that was widely used as a sensitizer in electrophotography. Its biological properties have also been investigated widely.[2]
References
- ^ Berneth, Horst (2008). "Methine Dyes and Pigments". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_487.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Chong, Curtis R.; Xu, Jing; Lu, Jun; Bhat, Shridhar; Sullivan, David J.; Liu, Jun O. (2007). "Inhibition of Angiogenesis by the Antifungal Drug Itraconazole". ACS Chemical Biology. 2 (4): 263–270. doi:10.1021/cb600362d. PMID 17432820.