Paul Schmitt P.S.3
| Paul Schmitt P.S.3 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | bomber/trainer |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Paul Schmitt |
| Designer | Paul Schmitt |
| Introduction | 1915[1] |
| Status | retired |
| Primary user | Aéronautique Militaire |
| Number built | 6[1] |
The Paul Schmitt P.S.3 was a French World War I biplane bomber that was built in small numbers but primarily used as a trainer.[1]
Development
The P.S.3 was unusual in that the entire wing cellule was designed to have its angle of incidence adjusted from 0° to 12° while in flight.[2] When set at the maximum, this gave the aircraft a pronounced back-stagger. This was possible because the wing was attached to the fuselage by a single pivot, and controlled by a jackscrew in the cockpit.[2] This allowed for an unusually broad speed range, so that a minimum speed of only 35 km/h (22 mph) was achieved.[2] The fuselage was built up from welded steel tubes, with a square cross section forward tapering to a triangle section aft.[2]
One example was built as a floatplane, however unlike most of the landplanes, it was powered by a 150 hp (110 kW) Canton Unné P9 liquid cooled radial in place of the Gnome rotaries normally used.
Operational history
Although intended as a bomber, it was only ever built in small numbers, and was quickly relegated to use as a trainer, partly because the Aéronautique Militaire had already chosen the Voisin III as their standard bomber.
Victorin Garaix set a number of speed and height records while carrying passengers in 1914.[3]
The floatplane was exported to a private buyer the US in 1916,[1] only to later be taken on strength by the United States Navy in April 1917 with the serial A-52, however it was used primarily as an instructional airframe at Pensacola for training groundcrew.[4]
Operators
Specifications (Paul Schmitt P.S.3)
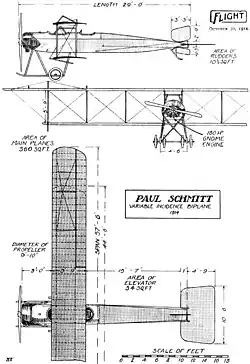
Data from Davilla, 1997, p.451
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 10.00 m (32 ft 10 in)
- Upper wingspan: 17.50 m (57 ft 5 in)
- Lower wingspan: 13.56 m (44 ft 6 in)
- Wing Chord: 1.75 m (5 ft 9 in)
- Height: 3.15 m (10 ft 4 in)
- Wing area: 49 m2 (530 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 650 kg (1,433 lb)
- Gross weight: 1,100 kg (2,425 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Gnome 14 Lambda-Lambda 14 cylinder double-row air-cooled rotary, 120 kW (160 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed Régy 301, 3.00 m (9 ft 10 in) diameter wood fixed pitch propeller[5]
Performance
- Maximum speed: 116 km/h (72 mph, 63 kn)
- Stall speed: 35 km/h (22 mph, 19 kn)
- Range: 460 km (290 mi, 250 nmi)
References
Citations
Bibliography
- Baugher, Joe (9 May 2019). "US Navy and US Marine Corps BuNos - First Series (A51 to A6001)". Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- Davilla, Dr. James J.; Soltan, Arthur (1997). French Aircraft of the First World War. Mountain View, CA: Flying Machines Press. ISBN 978-1891268090.
- Hartmann, Gérard (6 January 2015). "Les héliciers français" (PDF) (in French). Retrieved 5 August 2019.
- Stanley Spooner, ed. (30 October 1914). "The Paul Schmitt Biplane". Flight Magazine. No. 305 Volume VI/No.44. London, UK. pp. 1072–1074.