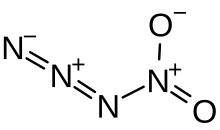
Nitryl azide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-diazonitramide
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| N3−NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 88.026 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Nitrosyl azide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
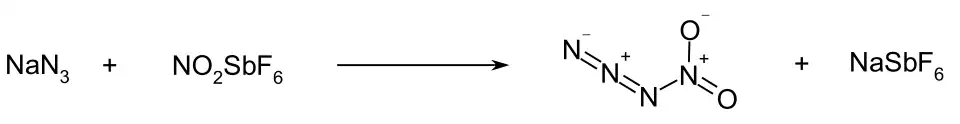
Nitryl azide (tetranitrogen dioxide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula N3−NO2. It is an unstable nitrogen oxide consisting of a covalent nitrogen–nitrogen bond between a nitro group and an azide group. It has been detected by infrared spectroscopy as a short-lived product of the reaction between sodium azide and nitronium hexafluoroantimonate:[1]
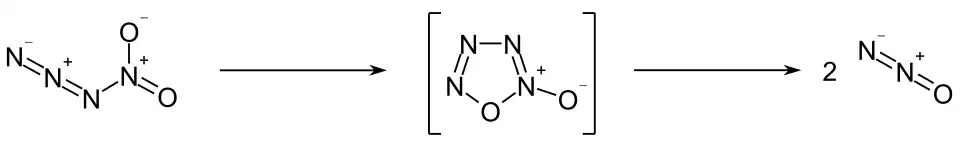
The compound quickly decomposes to form nitrous oxide. Calculations suggest that this process occurs via an oxatetrazole oxide intermediate:[2]
References
- ^ Doyle, Michael P.; Maciejko, James J.; Busman, Stanley C. (1973). "Reaction between azide and nitronium ions. Formation and decomposition of nitryl azide". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 95 (3): 952–953. Bibcode:1973JAChS..95..952D. doi:10.1021/ja00784a069.
- ^ Zeng, Xiaoqing; Ge, Maofo; Sun, Zheng; Bian, Jiang; Wang, Dianxun (2007). "Gaseous nitryl azide N4O2: A joint theoretical and experimental study". Journal of Molecular Structure. 840 (1–3): 59–65. Bibcode:2007JMoSt.840...59Z. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2006.11.034.