Kukoamines
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
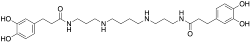
3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-N-[3-[4-[3-[3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoylamino]propylamino]butylamino]propyl]propanamide | |
| Other names
N(1),N(12)-bis(dihydrocaffeoyl)spermine
AC1NSXD9 BDBM50240622 DNC013917 C17615 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H42N4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 530.666 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Kukoamines are chemicals that are present in some plants including Lycium chinense, potatoes, and tomatoes.[2][3][4] The most prevalent example is kukoamine A; others include kukoamine B, C, and D.[5][6][7]
Chemically, kukoamines are catechols and also dihydrocaffeic acid derivatives of polyamines.[4]
References
- ^ CID 5318865 from PubChem
- ^ Lim, T. K. (2016-02-11). Edible Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Plants: Volume 12 Modified Stems, Roots, Bulbs. Springer. ISBN 9783319260655.
- ^ "Kukoamines Found in Potatoes". cabi.org. Retrieved 2017-04-07.
- ^ a b Parr, Adrian J.; Mellon, Fred A.; Colquhoun, Ian J.; Davies, Howard V. (2005). "Dihydrocaffeoyl Polyamines (Kukoamine and Allies) in Potato (Solanum tuberosum) Tubers Detected during Metabolite Profiling". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (13): 5461–6. doi:10.1021/jf050298i. PMID 15969534.
- ^ CID 10346914 from PubChem, entry for kukoamine B
- ^ CID 10052730 from PubChem, entry for kukoamine C
- ^ CID 10075692 from PubChem, entry for kukoamine D