"Hyperbolic curve" redirects here. For the geometric curve, see
Hyperbola .
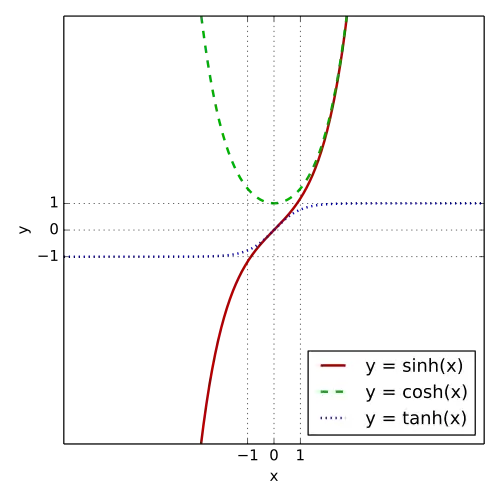
In mathematics , hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions , but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circle . Just as the points (cos t , sin t ) form a circle with a unit radius , the points (cosh t , sinh t ) form the right half of the unit hyperbola . Also, similarly to how the derivatives of sin(t ) and cos(t ) are cos(t ) and –sin(t ) respectively, the derivatives of sinh(t ) and cosh(t ) are cosh(t ) and sinh(t ) respectively.
Hyperbolic functions are used to express the angle of parallelism in hyperbolic geometry . They are used to express Lorentz boosts as hyperbolic rotations in special relativity . They also occur in the solutions of many linear differential equations (such as the equation defining a catenary ), cubic equations , and Laplace's equation in Cartesian coordinates . Laplace's equations are important in many areas of physics , including electromagnetic theory , heat transfer , and fluid dynamics .
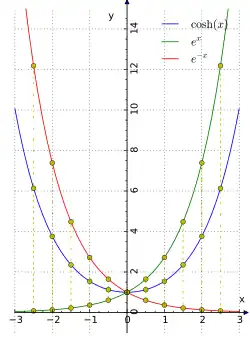
The basic hyperbolic functions are:[ 1]
hyperbolic sine "sinh " (),[ 2] hyperbolic cosine "cosh " (),[ 3] from which are derived:[ 4]
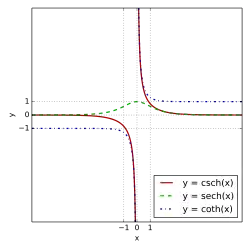
hyperbolic tangent "tanh " (),[ 5] hyperbolic cotangent "coth " (),[ 6] [ 7] hyperbolic secant "sech " (),[ 8] hyperbolic cosecant "csch " or "cosech " ([ 3] corresponding to the derived trigonometric functions.
The inverse hyperbolic functions are:
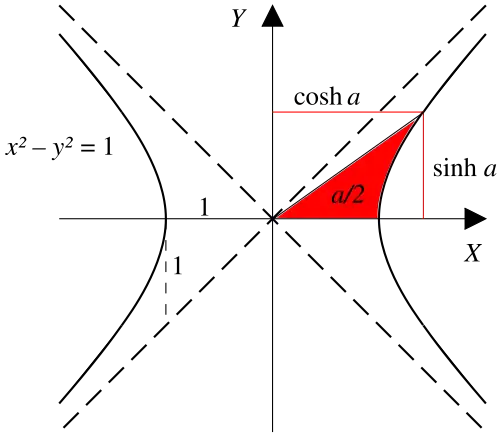
inverse hyperbolic sine "arsinh " (also denoted "sinh−1 ", "asinh " or sometimes "arcsinh ")[ 9] [ 10] [ 11] inverse hyperbolic cosine "arcosh " (also denoted "cosh−1 ", "acosh " or sometimes "arccosh ")inverse hyperbolic tangent "artanh " (also denoted "tanh−1 ", "atanh " or sometimes "arctanh ")inverse hyperbolic cotangent "arcoth " (also denoted "coth−1 ", "acoth " or sometimes "arccoth ")inverse hyperbolic secant "arsech " (also denoted "sech−1 ", "asech " or sometimes "arcsech ")inverse hyperbolic cosecant "arcsch " (also denoted "arcosech ", "csch−1 ", "cosech−1 ","acsch ", "acosech ", or sometimes "arccsch " or "arccosech ")A ray through the unit hyperbola x 2 − y 2 = 1(cosh a , sinh a ) , where a is twice the area between the ray, the hyperbola, and the x -axis. For points on the hyperbola below the x -axis, the area is considered negative (see animated version with comparison with the trigonometric (circular) functions). The hyperbolic functions take a real argument called a hyperbolic angle . The magnitude of a hyperbolic angle is the area of its hyperbolic sector to xy = 1. The hyperbolic functions may be defined in terms of the legs of a right triangle covering this sector.
In complex analysis , the hyperbolic functions arise when applying the ordinary sine and cosine functions to an imaginary angle. The hyperbolic sine and the hyperbolic cosine are entire functions . As a result, the other hyperbolic functions are meromorphic in the whole complex plane.
By Lindemann–Weierstrass theorem , the hyperbolic functions have a transcendental value for every non-zero algebraic value of the argument.[ 12]
History
The first known calculation of a hyperbolic trigonometry problem is attributed to Gerardus Mercator when issuing the Mercator map projection circa 1566. It requires tabulating solutions to a transcendental equation involving hyperbolic functions.[ 13]
The first to suggest a similarity between the sector of the circle and that of the hyperbola was Isaac Newton in his 1687 Principia Mathematica [ 14]
Roger Cotes suggested to modify the trigonometric functions using the imaginary unit
i
=
−
1
{\displaystyle i={\sqrt {-1}}}
spheroid from a prolate one.[ 14]
Hyperbolic functions were formally introduced in 1757 by Vincenzo Riccati .[ 14] [ 13] [ 15] Sc. Cc. sinus/cosinus circulare Sh. Ch. sinus/cosinus hyperbolico [ 14] Daviet de Foncenex showed the interchangeability of the trigonometric and hyperbolic functions using the imaginary unit and extended de Moivre's formula to hyperbolic functions.[ 15] [ 14]
During the 1760s, Johann Heinrich Lambert systematized the use functions and provided exponential expressions in various publications.[ 14] [ 15] [ 15] [ 16]
Notation
Definitions
Right triangles with legs proportional to sinh and cosh With hyperbolic angle u , the hyperbolic functions sinh and cosh can defined with the exponential function eu .[ 1] [ 4]
A
=
(
e
−
u
,
e
u
)
,
B
=
(
e
u
,
e
−
u
)
,
O
A
+
O
B
=
O
C
{\displaystyle A=(e^{-u},e^{u}),\ B=(e^{u},\ e^{-u}),\ OA+OB=OC}
Exponential definitions
sinh x is half the difference of ex e −x cosh x is the average of ex e −x Hyperbolic sine: the odd part of the exponential function, that is,
sinh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
2
=
e
2
x
−
1
2
e
x
=
1
−
e
−
2
x
2
e
−
x
.
{\displaystyle \sinh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{2}}={\frac {e^{2x}-1}{2e^{x}}}={\frac {1-e^{-2x}}{2e^{-x}}}.}
Hyperbolic cosine: the even part of the exponential function, that is,
cosh
x
=
e
x
+
e
−
x
2
=
e
2
x
+
1
2
e
x
=
1
+
e
−
2
x
2
e
−
x
.
{\displaystyle \cosh x={\frac {e^{x}+e^{-x}}{2}}={\frac {e^{2x}+1}{2e^{x}}}={\frac {1+e^{-2x}}{2e^{-x}}}.}
sinh , cosh and tanh csch , sech and coth Hyperbolic tangent:
tanh
x
=
sinh
x
cosh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
=
e
2
x
−
1
e
2
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle \tanh x={\frac {\sinh x}{\cosh x}}={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{2x}-1}{e^{2x}+1}}.}
Hyperbolic cotangent: for x ≠ 0
coth
x
=
cosh
x
sinh
x
=
e
x
+
e
−
x
e
x
−
e
−
x
=
e
2
x
+
1
e
2
x
−
1
.
{\displaystyle \coth x={\frac {\cosh x}{\sinh x}}={\frac {e^{x}+e^{-x}}{e^{x}-e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{2x}+1}{e^{2x}-1}}.}
Hyperbolic secant:
sech
x
=
1
cosh
x
=
2
e
x
+
e
−
x
=
2
e
x
e
2
x
+
1
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {sech} x={\frac {1}{\cosh x}}={\frac {2}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}={\frac {2e^{x}}{e^{2x}+1}}.}
Hyperbolic cosecant: for x ≠ 0
csch
x
=
1
sinh
x
=
2
e
x
−
e
−
x
=
2
e
x
e
2
x
−
1
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {csch} x={\frac {1}{\sinh x}}={\frac {2}{e^{x}-e^{-x}}}={\frac {2e^{x}}{e^{2x}-1}}.}
Differential equation definitions
The hyperbolic functions may be defined as solutions of differential equations : The hyperbolic sine and cosine are the solution (s , c ) of the system
c
′
(
x
)
=
s
(
x
)
,
s
′
(
x
)
=
c
(
x
)
,
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}c'(x)&=s(x),\\s'(x)&=c(x),\\\end{aligned}}}
s
(
0
)
=
0
,
c
(
0
)
=
1.
{\displaystyle s(0)=0,c(0)=1.}
(
a
e
x
+
b
e
−
x
,
a
e
x
−
b
e
−
x
)
{\displaystyle (ae^{x}+be^{-x},ae^{x}-be^{-x})}
sinh(x ) and cosh(x ) are also the unique solution of the equation f ″(x ) = f (x )f (0) = 1f ′(0) = 0f (0) = 0f ′(0) = 1
Complex trigonometric definitions
Hyperbolic functions may also be deduced from trigonometric functions with complex arguments:
Hyperbolic sine:[ 1]
sinh
x
=
−
i
sin
(
i
x
)
.
{\displaystyle \sinh x=-i\sin(ix).}
Hyperbolic cosine:[ 1]
cosh
x
=
cos
(
i
x
)
.
{\displaystyle \cosh x=\cos(ix).}
Hyperbolic tangent:
tanh
x
=
−
i
tan
(
i
x
)
.
{\displaystyle \tanh x=-i\tan(ix).}
Hyperbolic cotangent:
coth
x
=
i
cot
(
i
x
)
.
{\displaystyle \coth x=i\cot(ix).}
Hyperbolic secant:
sech
x
=
sec
(
i
x
)
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {sech} x=\sec(ix).}
Hyperbolic cosecant:
csch
x
=
i
csc
(
i
x
)
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {csch} x=i\csc(ix).}
where i is the imaginary unit with i 2 = −1
The above definitions are related to the exponential definitions via Euler's formula (See § Hyperbolic functions for complex numbers below).
Characterizing properties
Hyperbolic cosine
It can be shown that the area under the curve of the hyperbolic cosine (over a finite interval) is always equal to the arc length corresponding to that interval:[ 17]
area
=
∫
a
b
cosh
x
d
x
=
∫
a
b
1
+
(
d
d
x
cosh
x
)
2
d
x
=
arc length.
{\displaystyle {\text{area}}=\int _{a}^{b}\cosh x\,dx=\int _{a}^{b}{\sqrt {1+\left({\frac {d}{dx}}\cosh x\right)^{2}}}\,dx={\text{arc length.}}}
Hyperbolic tangent
The hyperbolic tangent is the (unique) solution to the differential equation f ′ = 1 − f 2 f (0) = 0[ 18] [ 19]
Useful relations
trigonometric identities . In fact, Osborn's rule [ 20]
θ
{\displaystyle \theta }
2
θ
{\displaystyle 2\theta }
3
θ
{\displaystyle 3\theta }
θ
{\displaystyle \theta }
φ
{\displaystyle \varphi }
expanding it completely in terms of integral powers of sines and cosines,
changing sine to sinh and cosine to cosh, and
switching the sign of every term containing a product of two sinhs. Odd and even functions:
sinh
(
−
x
)
=
−
sinh
x
cosh
(
−
x
)
=
cosh
x
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\sinh(-x)&=-\sinh x\\\cosh(-x)&=\cosh x\end{aligned}}}
Hence:
tanh
(
−
x
)
=
−
tanh
x
coth
(
−
x
)
=
−
coth
x
sech
(
−
x
)
=
sech
x
csch
(
−
x
)
=
−
csch
x
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\tanh(-x)&=-\tanh x\\\coth(-x)&=-\coth x\\\operatorname {sech} (-x)&=\operatorname {sech} x\\\operatorname {csch} (-x)&=-\operatorname {csch} x\end{aligned}}}
Thus, cosh x and sech x are even functions ; the others are odd functions .
arsech
x
=
arcosh
(
1
x
)
arcsch
x
=
arsinh
(
1
x
)
arcoth
x
=
artanh
(
1
x
)
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\operatorname {arsech} x&=\operatorname {arcosh} \left({\frac {1}{x}}\right)\\\operatorname {arcsch} x&=\operatorname {arsinh} \left({\frac {1}{x}}\right)\\\operatorname {arcoth} x&=\operatorname {artanh} \left({\frac {1}{x}}\right)\end{aligned}}}
Hyperbolic sine and cosine satisfy:
cosh
x
+
sinh
x
=
e
x
cosh
x
−
sinh
x
=
e
−
x
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\cosh x+\sinh x&=e^{x}\\\cosh x-\sinh x&=e^{-x}\end{aligned}}}
which are analogous to Euler's formula , and
cosh
2
x
−
sinh
2
x
=
1
{\displaystyle \cosh ^{2}x-\sinh ^{2}x=1}
which is analogous to the Pythagorean trigonometric identity .
One also has
sech
2
x
=
1
−
tanh
2
x
csch
2
x
=
coth
2
x
−
1
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\operatorname {sech} ^{2}x&=1-\tanh ^{2}x\\\operatorname {csch} ^{2}x&=\coth ^{2}x-1\end{aligned}}}
for the other functions.
Sums of arguments
sinh
(
x
+
y
)
=
sinh
x
cosh
y
+
cosh
x
sinh
y
cosh
(
x
+
y
)
=
cosh
x
cosh
y
+
sinh
x
sinh
y
tanh
(
x
+
y
)
=
tanh
x
+
tanh
y
1
+
tanh
x
tanh
y
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\sinh(x+y)&=\sinh x\cosh y+\cosh x\sinh y\\\cosh(x+y)&=\cosh x\cosh y+\sinh x\sinh y\\\tanh(x+y)&={\frac {\tanh x+\tanh y}{1+\tanh x\tanh y}}\\\end{aligned}}}
cosh
(
2
x
)
=
sinh
2
x
+
cosh
2
x
=
2
sinh
2
x
+
1
=
2
cosh
2
x
−
1
sinh
(
2
x
)
=
2
sinh
x
cosh
x
tanh
(
2
x
)
=
2
tanh
x
1
+
tanh
2
x
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\cosh(2x)&=\sinh ^{2}{x}+\cosh ^{2}{x}=2\sinh ^{2}x+1=2\cosh ^{2}x-1\\\sinh(2x)&=2\sinh x\cosh x\\\tanh(2x)&={\frac {2\tanh x}{1+\tanh ^{2}x}}\\\end{aligned}}}
Also:
sinh
x
+
sinh
y
=
2
sinh
(
x
+
y
2
)
cosh
(
x
−
y
2
)
cosh
x
+
cosh
y
=
2
cosh
(
x
+
y
2
)
cosh
(
x
−
y
2
)
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\sinh x+\sinh y&=2\sinh \left({\frac {x+y}{2}}\right)\cosh \left({\frac {x-y}{2}}\right)\\\cosh x+\cosh y&=2\cosh \left({\frac {x+y}{2}}\right)\cosh \left({\frac {x-y}{2}}\right)\\\end{aligned}}}
sinh
(
x
−
y
)
=
sinh
x
cosh
y
−
cosh
x
sinh
y
cosh
(
x
−
y
)
=
cosh
x
cosh
y
−
sinh
x
sinh
y
tanh
(
x
−
y
)
=
tanh
x
−
tanh
y
1
−
tanh
x
tanh
y
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\sinh(x-y)&=\sinh x\cosh y-\cosh x\sinh y\\\cosh(x-y)&=\cosh x\cosh y-\sinh x\sinh y\\\tanh(x-y)&={\frac {\tanh x-\tanh y}{1-\tanh x\tanh y}}\\\end{aligned}}}
Also:[ 21]
sinh
x
−
sinh
y
=
2
cosh
(
x
+
y
2
)
sinh
(
x
−
y
2
)
cosh
x
−
cosh
y
=
2
sinh
(
x
+
y
2
)
sinh
(
x
−
y
2
)
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\sinh x-\sinh y&=2\cosh \left({\frac {x+y}{2}}\right)\sinh \left({\frac {x-y}{2}}\right)\\\cosh x-\cosh y&=2\sinh \left({\frac {x+y}{2}}\right)\sinh \left({\frac {x-y}{2}}\right)\\\end{aligned}}}
sinh
(
x
2
)
=
sinh
x
2
(
cosh
x
+
1
)
=
sgn
x
cosh
x
−
1
2
cosh
(
x
2
)
=
cosh
x
+
1
2
tanh
(
x
2
)
=
sinh
x
cosh
x
+
1
=
sgn
x
cosh
x
−
1
cosh
x
+
1
=
e
x
−
1
e
x
+
1
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\sinh \left({\frac {x}{2}}\right)&={\frac {\sinh x}{\sqrt {2(\cosh x+1)}}}&&=\operatorname {sgn} x\,{\sqrt {\frac {\cosh x-1}{2}}}\\[6px]\cosh \left({\frac {x}{2}}\right)&={\sqrt {\frac {\cosh x+1}{2}}}\\[6px]\tanh \left({\frac {x}{2}}\right)&={\frac {\sinh x}{\cosh x+1}}&&=\operatorname {sgn} x\,{\sqrt {\frac {\cosh x-1}{\cosh x+1}}}={\frac {e^{x}-1}{e^{x}+1}}\end{aligned}}}
where sgn is the sign function .
If x ≠ 0[ 22]
tanh
(
x
2
)
=
cosh
x
−
1
sinh
x
=
coth
x
−
csch
x
{\displaystyle \tanh \left({\frac {x}{2}}\right)={\frac {\cosh x-1}{\sinh x}}=\coth x-\operatorname {csch} x}
sinh
2
x
=
1
2
(
cosh
2
x
−
1
)
cosh
2
x
=
1
2
(
cosh
2
x
+
1
)
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\sinh ^{2}x&={\tfrac {1}{2}}(\cosh 2x-1)\\\cosh ^{2}x&={\tfrac {1}{2}}(\cosh 2x+1)\end{aligned}}}
Inequalities
The following inequality is useful in statistics:[ 23]
cosh
(
t
)
≤
e
t
2
/
2
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {cosh} (t)\leq e^{t^{2}/2}.}
It can be proved by comparing the Taylor series of the two functions term by term.
Inverse functions as logarithms
arsinh
(
x
)
=
ln
(
x
+
x
2
+
1
)
arcosh
(
x
)
=
ln
(
x
+
x
2
−
1
)
x
≥
1
artanh
(
x
)
=
1
2
ln
(
1
+
x
1
−
x
)
|
x
|
<
1
arcoth
(
x
)
=
1
2
ln
(
x
+
1
x
−
1
)
|
x
|
>
1
arsech
(
x
)
=
ln
(
1
x
+
1
x
2
−
1
)
=
ln
(
1
+
1
−
x
2
x
)
0
<
x
≤
1
arcsch
(
x
)
=
ln
(
1
x
+
1
x
2
+
1
)
x
≠
0
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\operatorname {arsinh} (x)&=\ln \left(x+{\sqrt {x^{2}+1}}\right)\\\operatorname {arcosh} (x)&=\ln \left(x+{\sqrt {x^{2}-1}}\right)&&x\geq 1\\\operatorname {artanh} (x)&={\frac {1}{2}}\ln \left({\frac {1+x}{1-x}}\right)&&|x|<1\\\operatorname {arcoth} (x)&={\frac {1}{2}}\ln \left({\frac {x+1}{x-1}}\right)&&|x|>1\\\operatorname {arsech} (x)&=\ln \left({\frac {1}{x}}+{\sqrt {{\frac {1}{x^{2}}}-1}}\right)=\ln \left({\frac {1+{\sqrt {1-x^{2}}}}{x}}\right)&&0<x\leq 1\\\operatorname {arcsch} (x)&=\ln \left({\frac {1}{x}}+{\sqrt {{\frac {1}{x^{2}}}+1}}\right)&&x\neq 0\end{aligned}}}
Derivatives
d
d
x
sinh
x
=
cosh
x
d
d
x
cosh
x
=
sinh
x
d
d
x
tanh
x
=
1
−
tanh
2
x
=
sech
2
x
=
1
cosh
2
x
d
d
x
coth
x
=
1
−
coth
2
x
=
−
csch
2
x
=
−
1
sinh
2
x
x
≠
0
d
d
x
sech
x
=
−
tanh
x
sech
x
d
d
x
csch
x
=
−
coth
x
csch
x
x
≠
0
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\frac {d}{dx}}\sinh x&=\cosh x\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\cosh x&=\sinh x\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\tanh x&=1-\tanh ^{2}x=\operatorname {sech} ^{2}x={\frac {1}{\cosh ^{2}x}}\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\coth x&=1-\coth ^{2}x=-\operatorname {csch} ^{2}x=-{\frac {1}{\sinh ^{2}x}}&&x\neq 0\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\operatorname {sech} x&=-\tanh x\operatorname {sech} x\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\operatorname {csch} x&=-\coth x\operatorname {csch} x&&x\neq 0\end{aligned}}}
d
d
x
arsinh
x
=
1
x
2
+
1
d
d
x
arcosh
x
=
1
x
2
−
1
1
<
x
d
d
x
artanh
x
=
1
1
−
x
2
|
x
|
<
1
d
d
x
arcoth
x
=
1
1
−
x
2
1
<
|
x
|
d
d
x
arsech
x
=
−
1
x
1
−
x
2
0
<
x
<
1
d
d
x
arcsch
x
=
−
1
|
x
|
1
+
x
2
x
≠
0
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\frac {d}{dx}}\operatorname {arsinh} x&={\frac {1}{\sqrt {x^{2}+1}}}\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\operatorname {arcosh} x&={\frac {1}{\sqrt {x^{2}-1}}}&&1<x\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\operatorname {artanh} x&={\frac {1}{1-x^{2}}}&&|x|<1\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\operatorname {arcoth} x&={\frac {1}{1-x^{2}}}&&1<|x|\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\operatorname {arsech} x&=-{\frac {1}{x{\sqrt {1-x^{2}}}}}&&0<x<1\\{\frac {d}{dx}}\operatorname {arcsch} x&=-{\frac {1}{|x|{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}&&x\neq 0\end{aligned}}}
Second derivatives
Each of the functions sinh and cosh is equal to its second derivative , that is:
d
2
d
x
2
sinh
x
=
sinh
x
{\displaystyle {\frac {d^{2}}{dx^{2}}}\sinh x=\sinh x}
d
2
d
x
2
cosh
x
=
cosh
x
.
{\displaystyle {\frac {d^{2}}{dx^{2}}}\cosh x=\cosh x\,.}
All functions with this property are linear combinations of sinh and cosh , in particular the exponential functions
e
x
{\displaystyle e^{x}}
e
−
x
{\displaystyle e^{-x}}
[ 24]
Standard integrals
∫
sinh
(
a
x
)
d
x
=
a
−
1
cosh
(
a
x
)
+
C
∫
cosh
(
a
x
)
d
x
=
a
−
1
sinh
(
a
x
)
+
C
∫
tanh
(
a
x
)
d
x
=
a
−
1
ln
(
cosh
(
a
x
)
)
+
C
∫
coth
(
a
x
)
d
x
=
a
−
1
ln
|
sinh
(
a
x
)
|
+
C
∫
sech
(
a
x
)
d
x
=
a
−
1
arctan
(
sinh
(
a
x
)
)
+
C
∫
csch
(
a
x
)
d
x
=
a
−
1
ln
|
tanh
(
a
x
2
)
|
+
C
=
a
−
1
ln
|
coth
(
a
x
)
−
csch
(
a
x
)
|
+
C
=
−
a
−
1
arcoth
(
cosh
(
a
x
)
)
+
C
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\int \sinh(ax)\,dx&=a^{-1}\cosh(ax)+C\\\int \cosh(ax)\,dx&=a^{-1}\sinh(ax)+C\\\int \tanh(ax)\,dx&=a^{-1}\ln(\cosh(ax))+C\\\int \coth(ax)\,dx&=a^{-1}\ln \left|\sinh(ax)\right|+C\\\int \operatorname {sech} (ax)\,dx&=a^{-1}\arctan(\sinh(ax))+C\\\int \operatorname {csch} (ax)\,dx&=a^{-1}\ln \left|\tanh \left({\frac {ax}{2}}\right)\right|+C=a^{-1}\ln \left|\coth \left(ax\right)-\operatorname {csch} \left(ax\right)\right|+C=-a^{-1}\operatorname {arcoth} \left(\cosh \left(ax\right)\right)+C\end{aligned}}}
The following integrals can be proved using hyperbolic substitution :
∫
1
a
2
+
u
2
d
u
=
arsinh
(
u
a
)
+
C
∫
1
u
2
−
a
2
d
u
=
sgn
u
arcosh
|
u
a
|
+
C
∫
1
a
2
−
u
2
d
u
=
a
−
1
artanh
(
u
a
)
+
C
u
2
<
a
2
∫
1
a
2
−
u
2
d
u
=
a
−
1
arcoth
(
u
a
)
+
C
u
2
>
a
2
∫
1
u
a
2
−
u
2
d
u
=
−
a
−
1
arsech
|
u
a
|
+
C
∫
1
u
a
2
+
u
2
d
u
=
−
a
−
1
arcsch
|
u
a
|
+
C
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\int {{\frac {1}{\sqrt {a^{2}+u^{2}}}}\,du}&=\operatorname {arsinh} \left({\frac {u}{a}}\right)+C\\\int {{\frac {1}{\sqrt {u^{2}-a^{2}}}}\,du}&=\operatorname {sgn} {u}\operatorname {arcosh} \left|{\frac {u}{a}}\right|+C\\\int {\frac {1}{a^{2}-u^{2}}}\,du&=a^{-1}\operatorname {artanh} \left({\frac {u}{a}}\right)+C&&u^{2}<a^{2}\\\int {\frac {1}{a^{2}-u^{2}}}\,du&=a^{-1}\operatorname {arcoth} \left({\frac {u}{a}}\right)+C&&u^{2}>a^{2}\\\int {{\frac {1}{u{\sqrt {a^{2}-u^{2}}}}}\,du}&=-a^{-1}\operatorname {arsech} \left|{\frac {u}{a}}\right|+C\\\int {{\frac {1}{u{\sqrt {a^{2}+u^{2}}}}}\,du}&=-a^{-1}\operatorname {arcsch} \left|{\frac {u}{a}}\right|+C\end{aligned}}}
where C is the constant of integration .
Taylor series expressions
It is possible to express explicitly the Taylor series at zero (or the Laurent series , if the function is not defined at zero) of the above functions.
sinh
x
=
x
+
x
3
3
!
+
x
5
5
!
+
x
7
7
!
+
⋯
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
x
2
n
+
1
(
2
n
+
1
)
!
{\displaystyle \sinh x=x+{\frac {x^{3}}{3!}}+{\frac {x^{5}}{5!}}+{\frac {x^{7}}{7!}}+\cdots =\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {x^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)!}}}
convergent for every complex value of x . Since the function sinh x is odd , only odd exponents for x
cosh
x
=
1
+
x
2
2
!
+
x
4
4
!
+
x
6
6
!
+
⋯
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
x
2
n
(
2
n
)
!
{\displaystyle \cosh x=1+{\frac {x^{2}}{2!}}+{\frac {x^{4}}{4!}}+{\frac {x^{6}}{6!}}+\cdots =\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {x^{2n}}{(2n)!}}}
convergent for every complex value of x . Since the function cosh x is even , only even exponents for x occur in its Taylor series.
The sum of the sinh and cosh series is the infinite series expression of the exponential function .
The following series are followed by a description of a subset of their domain of convergence , where the series is convergent and its sum equals the function.
tanh
x
=
x
−
x
3
3
+
2
x
5
15
−
17
x
7
315
+
⋯
=
∑
n
=
1
∞
2
2
n
(
2
2
n
−
1
)
B
2
n
x
2
n
−
1
(
2
n
)
!
,
|
x
|
<
π
2
coth
x
=
x
−
1
+
x
3
−
x
3
45
+
2
x
5
945
+
⋯
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
2
2
n
B
2
n
x
2
n
−
1
(
2
n
)
!
,
0
<
|
x
|
<
π
sech
x
=
1
−
x
2
2
+
5
x
4
24
−
61
x
6
720
+
⋯
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
E
2
n
x
2
n
(
2
n
)
!
,
|
x
|
<
π
2
csch
x
=
x
−
1
−
x
6
+
7
x
3
360
−
31
x
5
15120
+
⋯
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
2
(
1
−
2
2
n
−
1
)
B
2
n
x
2
n
−
1
(
2
n
)
!
,
0
<
|
x
|
<
π
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\tanh x&=x-{\frac {x^{3}}{3}}+{\frac {2x^{5}}{15}}-{\frac {17x^{7}}{315}}+\cdots =\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }{\frac {2^{2n}(2^{2n}-1)B_{2n}x^{2n-1}}{(2n)!}},\qquad \left|x\right|<{\frac {\pi }{2}}\\\coth x&=x^{-1}+{\frac {x}{3}}-{\frac {x^{3}}{45}}+{\frac {2x^{5}}{945}}+\cdots =\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {2^{2n}B_{2n}x^{2n-1}}{(2n)!}},\qquad 0<\left|x\right|<\pi \\\operatorname {sech} x&=1-{\frac {x^{2}}{2}}+{\frac {5x^{4}}{24}}-{\frac {61x^{6}}{720}}+\cdots =\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {E_{2n}x^{2n}}{(2n)!}},\qquad \left|x\right|<{\frac {\pi }{2}}\\\operatorname {csch} x&=x^{-1}-{\frac {x}{6}}+{\frac {7x^{3}}{360}}-{\frac {31x^{5}}{15120}}+\cdots =\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {2(1-2^{2n-1})B_{2n}x^{2n-1}}{(2n)!}},\qquad 0<\left|x\right|<\pi \end{aligned}}}
where:
Infinite products and continued fractions
The following expansions are valid in the whole complex plane:
sinh
x
=
x
∏
n
=
1
∞
(
1
+
x
2
n
2
π
2
)
=
x
1
−
x
2
2
⋅
3
+
x
2
−
2
⋅
3
x
2
4
⋅
5
+
x
2
−
4
⋅
5
x
2
6
⋅
7
+
x
2
−
⋱
{\displaystyle \sinh x=x\prod _{n=1}^{\infty }\left(1+{\frac {x^{2}}{n^{2}\pi ^{2}}}\right)={\cfrac {x}{1-{\cfrac {x^{2}}{2\cdot 3+x^{2}-{\cfrac {2\cdot 3x^{2}}{4\cdot 5+x^{2}-{\cfrac {4\cdot 5x^{2}}{6\cdot 7+x^{2}-\ddots }}}}}}}}}
cosh
x
=
∏
n
=
1
∞
(
1
+
x
2
(
n
−
1
/
2
)
2
π
2
)
=
1
1
−
x
2
1
⋅
2
+
x
2
−
1
⋅
2
x
2
3
⋅
4
+
x
2
−
3
⋅
4
x
2
5
⋅
6
+
x
2
−
⋱
{\displaystyle \cosh x=\prod _{n=1}^{\infty }\left(1+{\frac {x^{2}}{(n-1/2)^{2}\pi ^{2}}}\right)={\cfrac {1}{1-{\cfrac {x^{2}}{1\cdot 2+x^{2}-{\cfrac {1\cdot 2x^{2}}{3\cdot 4+x^{2}-{\cfrac {3\cdot 4x^{2}}{5\cdot 6+x^{2}-\ddots }}}}}}}}}
tanh
x
=
1
1
x
+
1
3
x
+
1
5
x
+
1
7
x
+
⋱
{\displaystyle \tanh x={\cfrac {1}{{\cfrac {1}{x}}+{\cfrac {1}{{\cfrac {3}{x}}+{\cfrac {1}{{\cfrac {5}{x}}+{\cfrac {1}{{\cfrac {7}{x}}+\ddots }}}}}}}}}
Comparison with circular functions
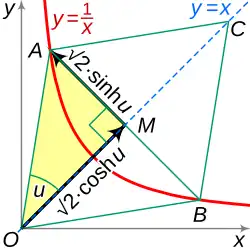
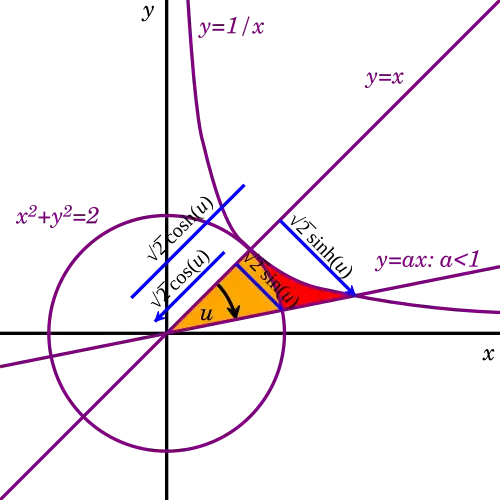
Circle and hyperbola tangent at (1,1) display geometry of circular functions in terms of circular sector area u and hyperbolic functions depending on hyperbolic sector area u . The hyperbolic functions represent an expansion of trigonometry beyond the circular functions . Both types depend on an argument , either circular angle or hyperbolic angle .
Since the area of a circular sector with radius r and angle u (in radians) is r 2 u /2u when r = √2 xy = 1 at (1,1). The yellow sector depicts an area and angle magnitude. Similarly, the yellow and red regions together depict a hyperbolic sector with area corresponding to hyperbolic angle magnitude.
The legs of the two right triangles with hypotenuse on the ray defining the angles are of length √2 times the circular and hyperbolic functions.
The hyperbolic angle is an invariant measure with respect to the squeeze mapping , just as the circular angle is invariant under rotation.[ 25]
The Gudermannian function gives a direct relationship between the circular functions and the hyperbolic functions that does not involve complex numbers.
The graph of the function
a
cosh
(
x
/
a
)
{\displaystyle a\cosh(x/a)}
is the catenary , the curve formed by a uniform flexible chain, hanging freely between two fixed points under uniform gravity.
Relationship to the exponential function
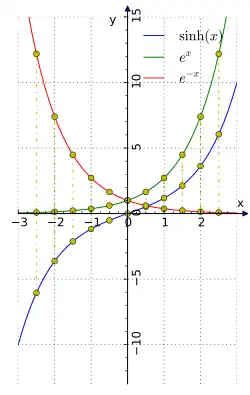
The decomposition of the exponential function in its even and odd parts gives the identities
e
x
=
cosh
x
+
sinh
x
,
{\displaystyle e^{x}=\cosh x+\sinh x,}
e
−
x
=
cosh
x
−
sinh
x
.
{\displaystyle e^{-x}=\cosh x-\sinh x.}
Euler's formula
e
i
x
=
cos
x
+
i
sin
x
,
{\displaystyle e^{ix}=\cos x+i\sin x,}
e
x
+
i
y
=
(
cosh
x
+
sinh
x
)
(
cos
y
+
i
sin
y
)
{\displaystyle e^{x+iy}=(\cosh x+\sinh x)(\cos y+i\sin y)}
general complex exponential function .
Additionally,
e
x
=
1
+
tanh
x
1
−
tanh
x
=
1
+
tanh
x
2
1
−
tanh
x
2
{\displaystyle e^{x}={\sqrt {\frac {1+\tanh x}{1-\tanh x}}}={\frac {1+\tanh {\frac {x}{2}}}{1-\tanh {\frac {x}{2}}}}}
Hyperbolic functions for complex numbers
Hyperbolic functions in the complex plane
sinh
(
z
)
{\displaystyle \sinh(z)}
cosh
(
z
)
{\displaystyle \cosh(z)}
tanh
(
z
)
{\displaystyle \tanh(z)}
coth
(
z
)
{\displaystyle \coth(z)}
sech
(
z
)
{\displaystyle \operatorname {sech} (z)}
csch
(
z
)
{\displaystyle \operatorname {csch} (z)}
Since the exponential function can be defined for any complex argument, we can also extend the definitions of the hyperbolic functions to complex arguments. The functions sinh z and cosh z are then holomorphic .
Relationships to ordinary trigonometric functions are given by Euler's formula for complex numbers:
e
i
x
=
cos
x
+
i
sin
x
e
−
i
x
=
cos
x
−
i
sin
x
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}e^{ix}&=\cos x+i\sin x\\e^{-ix}&=\cos x-i\sin x\end{aligned}}}
cosh
(
i
x
)
=
1
2
(
e
i
x
+
e
−
i
x
)
=
cos
x
sinh
(
i
x
)
=
1
2
(
e
i
x
−
e
−
i
x
)
=
i
sin
x
tanh
(
i
x
)
=
i
tan
x
cosh
(
x
+
i
y
)
=
cosh
(
x
)
cos
(
y
)
+
i
sinh
(
x
)
sin
(
y
)
sinh
(
x
+
i
y
)
=
sinh
(
x
)
cos
(
y
)
+
i
cosh
(
x
)
sin
(
y
)
tanh
(
x
+
i
y
)
=
tanh
(
x
)
+
i
tan
(
y
)
1
+
i
tanh
(
x
)
tan
(
y
)
cosh
x
=
cos
(
i
x
)
sinh
x
=
−
i
sin
(
i
x
)
tanh
x
=
−
i
tan
(
i
x
)
{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\cosh(ix)&={\frac {1}{2}}\left(e^{ix}+e^{-ix}\right)=\cos x\\\sinh(ix)&={\frac {1}{2}}\left(e^{ix}-e^{-ix}\right)=i\sin x\\\tanh(ix)&=i\tan x\\\cosh(x+iy)&=\cosh(x)\cos(y)+i\sinh(x)\sin(y)\\\sinh(x+iy)&=\sinh(x)\cos(y)+i\cosh(x)\sin(y)\\\tanh(x+iy)&={\frac {\tanh(x)+i\tan(y)}{1+i\tanh(x)\tan(y)}}\\\cosh x&=\cos(ix)\\\sinh x&=-i\sin(ix)\\\tanh x&=-i\tan(ix)\end{aligned}}}
Thus, hyperbolic functions are periodic with respect to the imaginary component, with period
2
π
i
{\displaystyle 2\pi i}
π
i
{\displaystyle \pi i}
See also
References
^ a b c d Weisstein, Eric W. "Hyperbolic Functions" . mathworld.wolfram.com . Retrieved 2020-08-29 .^ (1999) Collins Concise Dictionary , 4th edition, HarperCollins, Glasgow, ISBN 0 00 472257 4 , p. 1386
^ a b Collins Concise Dictionary , p. 328^ a b "Hyperbolic Functions" . www.mathsisfun.com . Retrieved 2020-08-29 .^ Collins Concise Dictionary , p. 1520^ Collins Concise Dictionary , p. 329^ tanh ^ Collins Concise Dictionary , p. 1340^ Woodhouse, N. M. J. (2003), Special Relativity , London: Springer, p. 71, ISBN 978-1-85233-426-0 ^ Abramowitz, Milton ; Stegun, Irene A. , eds. (1972), Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables Dover Publications , ISBN 978-0-486-61272-0 ^ Some examples of using arcsinh found in Google Books .^ Niven, Ivan (1985). Irrational Numbers . Vol. 11. Mathematical Association of America. ISBN 9780883850381 . JSTOR 10.4169/j.ctt5hh8zn . ^ a b George F. Becker; C. E. Van Orstrand (1909). Hyperbolic Functions ^ a b c d e f McMahon, James (1896). Hyperbolic Functions ^ a b c d Bradley, Robert E.; D'Antonio, Lawrence A.; Sandifer, Charles Edward. Euler at 300: an appreciation. Mathematical Association of America, 2007. Page 100.
^ Becker, Georg F. Hyperbolic functions. Read Books, 1931. Page xlviii.
^ N.P., Bali (2005). Golden Integral Calculus ISBN 81-7008-169-6 . ^ Steeb, Willi-Hans (2005). Nonlinear Workbook, The: Chaos, Fractals, Cellular Automata, Neural Networks, Genetic Algorithms, Gene Expression Programming, Support Vector Machine, Wavelets, Hidden Markov Models, Fuzzy Logic With C++, Java And Symbolicc++ Programs ISBN 978-981-310-648-2 . Extract of page 281 (using lambda=1) ^ Oldham, Keith B.; Myland, Jan; Spanier, Jerome (2010). An Atlas of Functions: with Equator, the Atlas Function Calculator ISBN 978-0-387-48807-3 . Extract of page 290 ^ Osborn, G. (July 1902). "Mnemonic for hyperbolic formulae" . The Mathematical Gazette 2 (34): 189. doi :10.2307/3602492 . JSTOR 3602492 . S2CID 125866575 . ^ Martin, George E. (1986). The foundations of geometry and the non-Euclidean plane (1st corr. ed.). New York: Springer-Verlag. p. 416. ISBN 3-540-90694-0 . ^ "Prove the identity tanh(x/2) = (cosh(x) - 1)/sinh(x)" . StackExchange (mathematics). Retrieved 24 January 2016 .^ Audibert, Jean-Yves (2009). "Fast learning rates in statistical inference through aggregation". The Annals of Statistics. p. 1627. [1] ^ Olver, Frank W. J. ; Lozier, Daniel M.; Boisvert, Ronald F.; Clark, Charles W., eds. (2010), "Hyperbolic functions" , NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions ISBN 978-0-521-19225-5 , MR 2723248 ^ Haskell, Mellen W. , "On the introduction of the notion of hyperbolic functions", Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 1 :6:155–9, full text
External links
Trigonometric and hyperbolic functions
Groups Other
Authority control databases
National Other