Funiculus (neuroanatomy)
| Funiculus | |
|---|---|
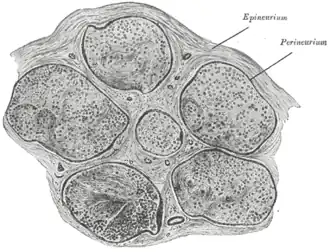 Transverse section of human tibial nerve. | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA98 | A14.1.00.010 |
| FMA | 76738 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
A funiculus is a small bundle of axons (nerve fibres), enclosed by the perineurium. A small nerve may consist of a single funiculus, but a larger nerve will have several funiculi collected together into larger bundles known as fascicles. Fascicles are bound together in a common membrane, the epineurium.[1][2]
Funiculi in the spinal cord are columns of white matter.[3][4] Examples include:
- Anterior funiculus of the spinal cord
- Lateral funiculus of the spinal cord
- Posterior funiculus of the spinal cord
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 728 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 728 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Gray, Henry; Lewis, Warren Harmon (1918). Anatomy of the human body. Harold B. Lee Library. Philadelphia : Lea & Febiger.
- ^ Siegel, A. & Sapru, H. (2011). Essential neuroscience. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- ^ "Spinal Cord White Matter".
- ^ "Ascending and descending tracts of the spinal cord". Kenhub. Retrieved 2022-10-06.