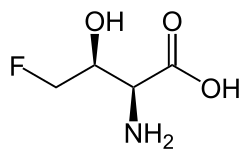
4-Fluoro-L-threonine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-Fluoro-L-threonine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3S)-2-Amino-4-fluoro-3-hydroxybutanoic acid | |
| Other names
4-Fluorothreonine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8FNO3 | |
| Molar mass | 137.110 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
4-Fluoro-l-threonine is an antibacterial produced by Streptomyces cattleya. It is formed by the fluorothreonine transaldolase catalysed transfer of fluoroacetaldehyde onto threonine.[1]
References
- ^ Murphy CD, O'Hagan D, Schaffrath C (2001). "Identification of a PLP-Dependent Threonine Transaldolase: A Novel Enzyme Involved in 4-Fluorothreonine Biosynthesis in Streptomyces cattleya This work was supported by the Biotechnological and Biological Sciences Research Council and the University of St Andrews". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 40 (23): 4479–4481. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20011203)40:23<4479::AID-ANIE4479>3.0.CO;2-1. PMID 12404452.