Flavone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Flavone[1]
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
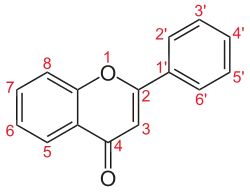
2-Phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one 2-Phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 157598 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.623 |
| EC Number |
|
| 1224858 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 222.243 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 96–97 °C (205–207 °F; 369–370 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Flavone is an organic compound with the formula C6H4OC3H(Ph)O. A white solid, flavone is a derivative of chromone with a phenyl (Ph) substituent adjacent to the ether group. The compound is of little direct practical importance, but substituted derivatives, the flavones and flavonoids are a large class of nutritionally important natural products.[2] Flavone can be prepared in the laboratory by cyclization of 2-hydroxacetophenone.[3] Isomeric with flavone is isoflavone, where the phenyl group is adjacent to the ketone.
References
- ^ https://iupac.qmul.ac.uk/flavonoid/index.html#Flv321
- ^ Gaspar, Alexandra; Matos, Maria João; Garrido, Jorge; Uriarte, Eugenio; Borges, Fernanda (2014). "Chromone: A Valid Scaffold in Medicinal Chemistry". Chemical Reviews. 114 (9): 4960–4992. doi:10.1021/cr400265z.
- ^ T. S. Wheeler (1952). "Flavone". Organic Syntheses. 32: 72. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.032.0072.