In mathematics , the Fibonacci polynomials are a polynomial sequence which can be considered as a generalization of the Fibonacci numbers . The polynomials generated in a similar way from the Lucas numbers are called Lucas polynomials .
Definition
These Fibonacci polynomials are defined by a recurrence relation :[ 1]
F
n
(
x
)
=
{
0
,
if
n
=
0
1
,
if
n
=
1
x
F
n
−
1
(
x
)
+
F
n
−
2
(
x
)
,
if
n
≥
2
{\displaystyle F_{n}(x)={\begin{cases}0,&{\mbox{if }}n=0\\1,&{\mbox{if }}n=1\\xF_{n-1}(x)+F_{n-2}(x),&{\mbox{if }}n\geq 2\end{cases}}}
The Lucas polynomials use the same recurrence with different starting values:[ 2]
L
n
(
x
)
=
{
2
,
if
n
=
0
x
,
if
n
=
1
x
L
n
−
1
(
x
)
+
L
n
−
2
(
x
)
,
if
n
≥
2.
{\displaystyle L_{n}(x)={\begin{cases}2,&{\mbox{if }}n=0\\x,&{\mbox{if }}n=1\\xL_{n-1}(x)+L_{n-2}(x),&{\mbox{if }}n\geq 2.\end{cases}}}
They can be defined for negative indices by[ 3]
F
−
n
(
x
)
=
(
−
1
)
n
−
1
F
n
(
x
)
,
{\displaystyle F_{-n}(x)=(-1)^{n-1}F_{n}(x),}
L
−
n
(
x
)
=
(
−
1
)
n
L
n
(
x
)
.
{\displaystyle L_{-n}(x)=(-1)^{n}L_{n}(x).}
The Fibonacci polynomials form a sequence of orthogonal polynomials with
A
n
=
C
n
=
1
{\displaystyle A_{n}=C_{n}=1}
B
n
=
0
{\displaystyle B_{n}=0}
Examples
The first few Fibonacci polynomials are:
F
0
(
x
)
=
0
{\displaystyle F_{0}(x)=0\,}
F
1
(
x
)
=
1
{\displaystyle F_{1}(x)=1\,}
F
2
(
x
)
=
x
{\displaystyle F_{2}(x)=x\,}
F
3
(
x
)
=
x
2
+
1
{\displaystyle F_{3}(x)=x^{2}+1\,}
F
4
(
x
)
=
x
3
+
2
x
{\displaystyle F_{4}(x)=x^{3}+2x\,}
F
5
(
x
)
=
x
4
+
3
x
2
+
1
{\displaystyle F_{5}(x)=x^{4}+3x^{2}+1\,}
F
6
(
x
)
=
x
5
+
4
x
3
+
3
x
{\displaystyle F_{6}(x)=x^{5}+4x^{3}+3x\,}
The first few Lucas polynomials are:
L
0
(
x
)
=
2
{\displaystyle L_{0}(x)=2\,}
L
1
(
x
)
=
x
{\displaystyle L_{1}(x)=x\,}
L
2
(
x
)
=
x
2
+
2
{\displaystyle L_{2}(x)=x^{2}+2\,}
L
3
(
x
)
=
x
3
+
3
x
{\displaystyle L_{3}(x)=x^{3}+3x\,}
L
4
(
x
)
=
x
4
+
4
x
2
+
2
{\displaystyle L_{4}(x)=x^{4}+4x^{2}+2\,}
L
5
(
x
)
=
x
5
+
5
x
3
+
5
x
{\displaystyle L_{5}(x)=x^{5}+5x^{3}+5x\,}
L
6
(
x
)
=
x
6
+
6
x
4
+
9
x
2
+
2.
{\displaystyle L_{6}(x)=x^{6}+6x^{4}+9x^{2}+2.\,}
Properties
The degree of F n n − 1 and the degree of L n n . The Fibonacci and Lucas numbers are recovered by evaluating the polynomials at x = 1; Pell numbers are recovered by evaluating F n x = 2. The ordinary generating functions for the sequences are:[ 4]
∑
n
=
0
∞
F
n
(
x
)
t
n
=
t
1
−
x
t
−
t
2
{\displaystyle \sum _{n=0}^{\infty }F_{n}(x)t^{n}={\frac {t}{1-xt-t^{2}}}}
∑
n
=
0
∞
L
n
(
x
)
t
n
=
2
−
x
t
1
−
x
t
−
t
2
.
{\displaystyle \sum _{n=0}^{\infty }L_{n}(x)t^{n}={\frac {2-xt}{1-xt-t^{2}}}.}
The polynomials can be expressed in terms of Lucas sequences as
F
n
(
x
)
=
U
n
(
x
,
−
1
)
,
{\displaystyle F_{n}(x)=U_{n}(x,-1),\,}
L
n
(
x
)
=
V
n
(
x
,
−
1
)
.
{\displaystyle L_{n}(x)=V_{n}(x,-1).\,}
They can also be expressed in terms of Chebyshev polynomials
T
n
(
x
)
{\displaystyle {\mathcal {T}}_{n}(x)}
U
n
(
x
)
{\displaystyle {\mathcal {U}}_{n}(x)}
F
n
(
x
)
=
i
n
−
1
⋅
U
n
−
1
(
−
i
x
2
)
,
{\displaystyle F_{n}(x)=i^{n-1}\cdot {\mathcal {U}}_{n-1}({\tfrac {-ix}{2}}),\,}
L
n
(
x
)
=
2
⋅
i
n
⋅
T
n
(
−
i
x
2
)
,
{\displaystyle L_{n}(x)=2\cdot i^{n}\cdot {\mathcal {T}}_{n}({\tfrac {-ix}{2}}),\,}
where
i
{\displaystyle i}
imaginary unit .
Identities
As particular cases of Lucas sequences, Fibonacci polynomials satisfy a number of identities, such as[ 3]
F
m
+
n
(
x
)
=
F
m
+
1
(
x
)
F
n
(
x
)
+
F
m
(
x
)
F
n
−
1
(
x
)
{\displaystyle F_{m+n}(x)=F_{m+1}(x)F_{n}(x)+F_{m}(x)F_{n-1}(x)\,}
L
m
+
n
(
x
)
=
L
m
(
x
)
L
n
(
x
)
−
(
−
1
)
n
L
m
−
n
(
x
)
{\displaystyle L_{m+n}(x)=L_{m}(x)L_{n}(x)-(-1)^{n}L_{m-n}(x)\,}
F
n
+
1
(
x
)
F
n
−
1
(
x
)
−
F
n
(
x
)
2
=
(
−
1
)
n
{\displaystyle F_{n+1}(x)F_{n-1}(x)-F_{n}(x)^{2}=(-1)^{n}\,}
F
2
n
(
x
)
=
F
n
(
x
)
L
n
(
x
)
.
{\displaystyle F_{2n}(x)=F_{n}(x)L_{n}(x).\,}
Closed form expressions, similar to Binet's formula are:[ 3]
F
n
(
x
)
=
α
(
x
)
n
−
β
(
x
)
n
α
(
x
)
−
β
(
x
)
,
L
n
(
x
)
=
α
(
x
)
n
+
β
(
x
)
n
,
{\displaystyle F_{n}(x)={\frac {\alpha (x)^{n}-\beta (x)^{n}}{\alpha (x)-\beta (x)}},\,L_{n}(x)=\alpha (x)^{n}+\beta (x)^{n},}
where
α
(
x
)
=
x
+
x
2
+
4
2
,
β
(
x
)
=
x
−
x
2
+
4
2
{\displaystyle \alpha (x)={\frac {x+{\sqrt {x^{2}+4}}}{2}},\,\beta (x)={\frac {x-{\sqrt {x^{2}+4}}}{2}}}
are the solutions (in t ) of
t
2
−
x
t
−
1
=
0.
{\displaystyle t^{2}-xt-1=0.\,}
For Lucas Polynomials n > 0, we have
L
n
(
x
)
=
∑
k
=
0
⌊
n
/
2
⌋
n
n
−
k
(
n
−
k
k
)
x
n
−
2
k
.
{\displaystyle L_{n}(x)=\sum _{k=0}^{\lfloor n/2\rfloor }{\frac {n}{n-k}}{\binom {n-k}{k}}x^{n-2k}.}
A relationship between the Fibonacci polynomials and the standard basis polynomials is given by[ 5]
x
n
=
F
n
+
1
(
x
)
+
∑
k
=
1
⌊
n
/
2
⌋
(
−
1
)
k
[
(
n
k
)
−
(
n
k
−
1
)
]
F
n
+
1
−
2
k
(
x
)
.
{\displaystyle x^{n}=F_{n+1}(x)+\sum _{k=1}^{\lfloor n/2\rfloor }(-1)^{k}\left[{\binom {n}{k}}-{\binom {n}{k-1}}\right]F_{n+1-2k}(x).}
For example,
x
4
=
F
5
(
x
)
−
3
F
3
(
x
)
+
2
F
1
(
x
)
{\displaystyle x^{4}=F_{5}(x)-3F_{3}(x)+2F_{1}(x)\,}
x
5
=
F
6
(
x
)
−
4
F
4
(
x
)
+
5
F
2
(
x
)
{\displaystyle x^{5}=F_{6}(x)-4F_{4}(x)+5F_{2}(x)\,}
x
6
=
F
7
(
x
)
−
5
F
5
(
x
)
+
9
F
3
(
x
)
−
5
F
1
(
x
)
{\displaystyle x^{6}=F_{7}(x)-5F_{5}(x)+9F_{3}(x)-5F_{1}(x)\,}
x
7
=
F
8
(
x
)
−
6
F
6
(
x
)
+
14
F
4
(
x
)
−
14
F
2
(
x
)
{\displaystyle x^{7}=F_{8}(x)-6F_{6}(x)+14F_{4}(x)-14F_{2}(x)\,}
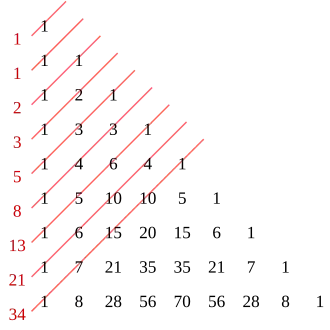
Combinatorial interpretation
The coefficients of the Fibonacci polynomials can be read off from a left-justified Pascal's triangle following the diagonals (shown in red). The sums of the coefficients are the Fibonacci numbers. If F (n ,k ) is the coefficient of xk in Fn (x ), namely
F
n
(
x
)
=
∑
k
=
0
n
F
(
n
,
k
)
x
k
,
{\displaystyle F_{n}(x)=\sum _{k=0}^{n}F(n,k)x^{k},\,}
then F (n ,k ) is the number of ways an n −1 by 1 rectangle can be tiled with 2 by 1 dominoes and 1 by 1 squares so that exactly k squares are used.[ 1] F (n ,k ) is the number of ways of writing n −1 as an ordered sum involving only 1 and 2, so that 1 is used exactly k times. For example F(6,3)=4 and 5 can be written in 4 ways, 1+1+1+2, 1+1+2+1, 1+2+1+1, 2+1+1+1, as a sum involving only 1 and 2 with 1 used 3 times. By counting the number of times 1 and 2 are both used in such a sum, it is evident that
F
(
n
,
k
)
=
{
(
1
2
(
n
+
k
−
1
)
k
)
if
n
≢
k
(
mod
2
)
,
0
else
.
{\displaystyle F(n,k)={\begin{cases}\displaystyle {\binom {{\frac {1}{2}}(n+k-1)}{k}}&{\text{if }}n\not \equiv k{\pmod {2}},\\[12pt]0&{\text{else}}.\end{cases}}}
This gives a way of reading the coefficients from Pascal's triangle as shown on the right.
References
Benjamin, Arthur T. ; Quinn, Jennifer J. (2003). "Fibonacci and Lucas Polynomial". Proofs that Really Count: The Art of Combinatorial Proof . Dolciani Mathematical Expositions. Vol. 27. Mathematical Association of America . p. 141 . ISBN 978-0-88385-333-7 .Philippou, Andreas N. (2001) [1994], "Fibonacci polynomials" , Encyclopedia of Mathematics EMS Press Philippou, Andreas N. (2001) [1994], "Lucas polynomials" , Encyclopedia of Mathematics EMS Press Weisstein, Eric W. "Lucas Polynomial" . MathWorld Jin, Z. On the Lucas polynomials and some of their new identities. Advances in Differential Equations 2018, 126 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-018-1527-9
Further reading
Hoggatt, V. E. ; Bicknell, Marjorie (1973). "Roots of Fibonacci polynomials". Fibonacci Quarterly 11 : 271– 274. ISSN 0015-0517 . MR 0332645 .Hoggatt, V. E.; Long, Calvin T. (1974). "Divisibility properties of generalized Fibonacci Polynomials". Fibonacci Quarterly 12 : 113. MR 0352034 . Ricci, Paolo Emilio (1995). "Generalized Lucas polynomials and Fibonacci polynomials". Rivista di Matematica della Università di Parma . V. Ser. 4 : 137– 146. MR 1395332 . Yuan, Yi; Zhang, Wenpeng (2002). "Some identities involving the Fibonacci Polynomials". Fibonacci Quarterly . 40 (4): 314. MR 1920571 . Cigler, Johann (2003). "q-Fibonacci polynomials". Fibonacci Quarterly (41): 31– 40. MR 1962279 .
External links