Lonicera xylosteum
| Lonicera xylosteum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Dipsacales |
| Family: | Caprifoliaceae |
| Genus: | Lonicera |
| Species: | L. xylosteum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lonicera xylosteum | |
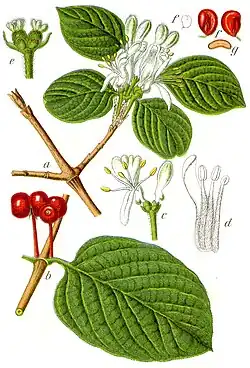
Lonicera xylosteum, commonly known as fly honeysuckle,[1] European fly honeysuckle, dwarf honeysuckle[2] or fly woodbine is a deciduous shrub.[1]
Its fruit persists for an average of 15.4 days, and bears an average of 4.5 seeds per fruit. Fruits average 88.6% water, and their dry weight includes 43.4% carbohydrates and 1.2% lipids.[3]
The glossy red (or occasionally yellow) berries of this shrub are mildly poisonous to humans – children who ingest a large number (c. 30) of berries may experience abdominal pain and vomiting.[4]
References
- ^ a b "Fly honeysuckle". RHS Gardening. Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 31 August 2017.
- ^ "Plants profile for Lonicera xylosteum". Plants database. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Retrieved 31 August 2017.
- ^ Ehrlén & Eriksson 1991.
- ^ "Lonicera xylosteum". Canadian Poisonous Plants Information System. Canadian Biodiversity Information Facility. Retrieved 31 August 2017.
Bibliography
- Ehrlén, Johan; Eriksson, Ove (1991). "Phenological variation in fruit characteristics in vertebrate-dispersed plants". Oecologia. 86 (4): 463–470. doi:10.1007/BF00318311. ISSN 0029-8549.