Copper(II) tetrafluoroborate
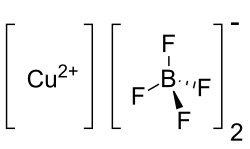 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Copper(II) tetrafluoroborate
| |
| Other names
Cupric tetrafluoroborate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.049.037 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Cu(BF4)2 | |
| Molar mass | 237.155 g/mol |
| Appearance | blue crystal |
| soluble in water | |
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
TWA 100 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Copper(II) chloride Copper(II) oxide Copper(II) triflate |
Other cations
|
Sodium tetrafluoroborate Lithium tetrafluoroborate Silver tetrafluoroborate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Copper(II) tetrafluoroborate or cupric tetrafluoroborate is any inorganic compound with the formula Cu(H2O)x(BF4)2. As usually encountered, it is assumed to be the hexahydrate (x = 6),[3] but this salt can be partially dehydrated to the tetrahydrate.[4] Regardless, these compounds are aquo complexes of copper in its +2 oxidation state, with two weakly coordinating tetrafluoroborate anions.
The compound is used in organic synthesis, e.g. as a Lewis acid for Diels Alder reactions, for cyclopropanation of alkenes with diazo reagents, and as a Lewis Acid in Meinwald Rearrangement reactions on Epoxides.[5] In the former two applications, the copper(II) is reduced to a copper(I) catalyst.[4][6] The compound is also used for copper electroplating in fluoroborate-based plating baths.[7]
References
- ^ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 4–56, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0150". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Vakulka, A., Goreshnik, E. Copper(II) Tetrafluoroborate Hexahydrate: Preparation, Structure and Raman Spectrum. J Chem Crystallogr 54, 157–162 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10870-024-01008-3
- ^ a b Ilhyong Ryu, Noboru Sonoda, "Copper(II) Tetrafluoroborate" Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 2001, John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rc249
- ^ Robinson, Mathew W.C.; Pillinger, Kathryn S.; Graham, Andrew E. (August 2006). "Highly efficient Meinwald rearrangement reactions of epoxides catalyzed by copper tetrafluoroborate". Tetrahedron Letters. 47 (33): 5919–5921. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2006.06.055.
- ^ Copper(II) Tetrafluorborate, chemicalland21.com
- ^ Barauskas, Romualdas "Ron" (January 1, 2000). "Copper plating". Metal Finishing. 98 (1): 234–247. doi:10.1016/S0026-0576(00)80330-X. ISSN 0026-0576. Retrieved July 21, 2022.