Bistrifluron
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
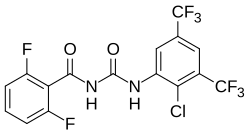
| IUPAC name
N-[[2-Chloro-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.118.415 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H7ClF8N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 446.68 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Bistrifluron is an insecticide of the benzoylurea class.[1] It is used to control chewing insects such as aphids, whiteflies, caterpillars, and termites.[2][3][4] It is not highly toxic to mammals, but bioaccumulation may be a concern.[2] It has a low level of toxicity to birds and moderate to high toxicity to most aquatic animals, honeybees, and earthworms.[2]
References
- ^ "Bistrifluron fact sheet".
- ^ a b c "Bistrifluron". Pesticide Properties DataBase. University of Hertforshire.
- ^ Kim, Min-Ki; Kim, Hak-Yong; Seo, Dong-Kyu; Yoon, Changmann; Kim, Gil-Hah (2007). "Insecticidal Properties of Bistrifluron, Benzoylphenylurea Insecticide, against Cotton Caterpillar, Palpita indica (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae)". Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology. 10 (3): 269–274. Bibcode:2007JAsPE..10..269K. doi:10.1016/S1226-8615(08)60362-3.
- ^ Webb, Garry (2017). "Elimination of Coptotermes lacteus (Froggatt) (Blattodea: Rhinotemitidae) Colonies Using Bistrifluron Bait Applied through In-Ground Bait Stations Surrounding Mounds". Insects. 8 (3): 98. doi:10.3390/insects8030098. PMC 5620718. PMID 28895934.