Benz Bz.IV
| Bz.IV | |
|---|---|
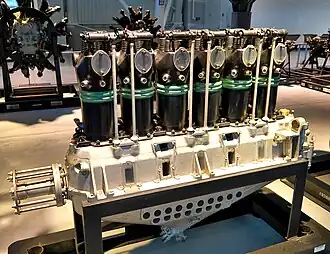
| |
| A Benz Bz.IV at the National Air and Space Museum's Udvar-Hazy Center (2017) | |
| Type | Inline piston engine |
| National origin | Germany |
| Manufacturer | Benz |
| First run | c. 1916 |
| Number built | 6,400 |
| Developed from | Benz Bz.III |
The Benz Bz.IV was a German six-cylinder, water-cooled, inline engine developed for aircraft use. Deliveries began in 1916, and some 6,400 were produced.
Design and development
The Bz.IV was a dual-camshaft design, with two intake and two exhaust valves per cylinder. The cylinders were cast iron surrounded by a sheet metal cooling jacket. The crankcase was aluminium and pistons were initially steel but later versions had aluminium pistons. A high compression version of the engine (Bz IVsü) was produced from 1917 onwards[1]. In February 1918, pistons from a Bz.IV were the first captured aluminium pistons to be examined by the British Ministry of Munitions.[2]
Variants
- IV
- (1916) Main production variant produced by Benz & Cie.
- IVmarta
- (1916) Licensed production of the Benz Bz.IV in Austria-Hungary by Magyar Automobil Részvény Társaság Arad (MARTA). The Marta produced version was heavier and had a lower compression ratio than the German original.
- IVsü
- (1917) Overcompressed version producing 205 kW (275 hp) at altitudes above 2,000 m (6,562 ft). Also known as the IVs, IVü or IVaü. The "ü" in the model description stands for überverdichtet (German: "overcompressed”) while the "s" denotes the use of steel cylinder liners.[1]
Applications
- AEG C.VI
- AEG J.I
- AGO C.IV
- Albatros C.VII
- Albatros C.XIV
- Albatros J.I
- Chitty 2 (racing car)
- DFW C.V
- Dobi-II
- Friedrichshafen FF.49
- Friedrichshafen G.II
- Halberstadt C.III
- Halberstadt C.V
- Junkers J.I
- LFG Roland C.III
- LVG C.VI
- NAVO RK-P4/220
- Pfalz D.XII
- Pfalz D.XIV
- Siemens-Schuckert R.III
- Siemens-Schuckert R.IV
- Siemens-Schuckert R.V
- Siemens-Schuckert R.VI
- Zeppelin-Staaken R.IV
- Zeppelin-Staaken R.XVI
Specifications
Data from [3]
General characteristics
- Type: 6-cylinder, water-cooled, inline aircraft piston engine
- Bore: 145 mm (5.7 in)
- Stroke: 190 mm (7.5 in)
- Displacement: 18.825 L (1,148.8 cu in)
- Length: 1,990 mm (78.3 in)
- Width: 530 mm (20.9 in)
- Height: 1,150 mm (45.3 in)
- Dry weight: 370 kg (815.7 lb)
Components
- Valvetrain: Twin inlet and exhaust valves operated by pushrod actuated double rockers
- Fuel system: Two Benz 2-jet carburettors feeding three cylinders each
- Fuel type: Gasoline specific gravity 0.72
- Oil system: Pressure feed at 0.2 MPa (28 psi): 50% Vacuum Heavy, 50% Sternol
- Cooling system: Water-cooled
Performance
- Power output: 170 kW (228.0 hp) at 1,400 rpm
- Specific power: 9.1 kW/L (0.2 hp/cu in)
- Compression ratio: 4.91:1
- Fuel consumption: 85.2 L (150 imp pt) / hour
- Specific fuel consumption: 0.495 L/kW/hr (0.65 pts/hp/hour)
- Oil consumption: 2.6 L (4.5 imp pt) / hour
- Power-to-weight ratio: 0.3796 kW/kg (0.231 hp/lb)
See also
Related lists
References
- ^ a b Düsing, Michael (2022). German & Austro-Hungarian Aero Engines of WW1. Vol. 1. Aeronaut Books. pp. 197–205. ISBN 9781953201515.
- ^ "Report on Aluminium Pistons from 230 HP Benz Engines". Flight. 4 July 1918.
- ^ Grey, C.G. (1969). Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1919 (Facsimile ed.). David & Charles (Publishing) Limited. pp. 1b to 145b. ISBN 978-0-7153-4647-1.
Bibliography
- Grey, C.G. (1969). Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1919 (Facsimile ed.). David & Charles (Publishing) Limited. pp. 1b to 145b. ISBN 978-0-7153-4647-1.
- Kroschel, Gunter and Helmust Stützer. (1977) Die deutschen Militarflugzeuge 1910-1918 Wilhelmshaven: Lohse-Eissing Mittler.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Benz Bz.IV.