6-EAPB
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
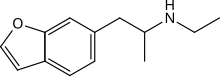
| Formula | C13H17NO |
| Molar mass | 203.285 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
6-EAPB (1-(benzofuran-6-yl)-N-ethylpropan-2-amine) is a potentially psychedelic and potentially entactogenic drug of the benzofuran class;[1] it is structurally related to 6-APB and MDMA.
Legality
As an N-ethyl derivative of 6-APB, 6-EAPB fell outside the scope of the Temporary Class Drug ban issued by the Home Office on June 10, 2013.[2] The ACMD has advised that 6-EAPB (and other benzofurans) are moved to Class B,[3] this came into action on 10 June 2014.[4]
References
- ^ Taschwer M, Hofer MG, Schmid MG (October 2014). "Enantioseparation of benzofurys and other novel psychoactive compounds by CE and sulfobutylether β-cyclodextrin as chiral selector added to the BGE". Electrophoresis. 35 (19): 2793–2799. doi:10.1002/elps.201400164. PMID 24930967. S2CID 2937770.
- ^ "Temporary class drug order on benzofury and NBOMe compounds". Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ^ "ACMD recommends permanent ban on two "legal highs"". Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ^ "Ban on NBOMe and benzofurans comes into force". Retrieved 15 June 2015.
| Phenethylamines |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Phentermines |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Cathinones |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Phenylisobutylamines (and further-extended) | |||||||||||||||||
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Cyclized phenethylamines |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Related compounds |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 unless otherwise noted. Additional terms may apply for the media files.