2-Chloro-6-fluorotoluene
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-chloro-3-fluoro-2-methylbenzene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.494 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6ClF | |
| Molar mass | 144.57 g·mol−1 |
| Boiling point | 154–156 °C (309–313 °F) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H226, H302, H312, H315, H332, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P321, P330, P362+P364, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 46 °C (115 °F) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
2-Chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde, toluene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
2-Chloro-6-fluorotoluene (CFT) is a halogenated derivative of toluene that is used as an intermediate in numerous organic syntheses.[1][2]
Uses
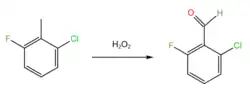
CFT is used to prepare 2-chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde via oxidation with hydrogen peroxide, which forms an aldehyde group.[2]
CFT is also used in the preparation of 4-chloro-1H-indazole.[1]
References
- ^ a b Meng, Ge; Yang, Tao; Liu, Yang (2011). "An Improved Preparation of 4-Chloro-1 H -indazole". Organic Preparations and Procedures International. 43 (4): 354–359. doi:10.1080/00304948.2011.594005. ISSN 0030-4948. S2CID 96965570.
- ^ a b Bunnett, J. F.; Miles, J. H.; Nahabedian, K. V. (1961). "Kinetics and Mechanism of the Alkali Cleavage of 2,6-Dihalobenzaldehydes 1". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 83 (11): 2512–2516. doi:10.1021/ja01472a022. ISSN 0002-7863.