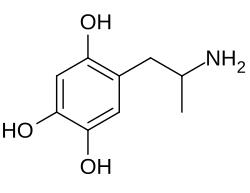
2,4,5-Trihydroxyamphetamine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-(2-Aminopropyl)benzene-1,2,4-triol | |
| Other names
THA
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H13NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 183.207 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
2,4,5-Trihydroxyamphetamine (THA) is a neurotoxin and a metabolite of MDMA. It comes from the ring-hydroxylation of 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA).
In one paper, it was shown to reduce hippocampal tryptophan hydroxylase activity by 54% after short-term treatment.[1] In another study, it was shown to significantly reduce striatal tyrosine hydroxylase activity.[2]
See also
- 2,4,5-Trihydroxymethamphetamine (THMA)
- 3,4-Dihydroxyamphetamine (HHA; α-methyldopamine)
- 3,4-Dihydroxymethamphetamine (HHMA; α-methylepinine)
- 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyamphetamine (HMA)
- 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxymethamphetamine (HMMA)
References
- ^ Elayan, I.; Gibb, J. W.; Hanson, G. R.; Lim, H. K.; Foltz, R. L.; Johnson, M. (May 1993). "Short-term effects of 2,4,5-trihydroxyamphetamine, 2,4,5-trihydroxymethamphetamine and 3,4-dihydroxymethamphetamine on central tryptophan hydroxylase activity". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 265 (2): 813–8. PMID 8496826.
- ^ Elayan I, Gibb JW, Hanson GR, Lim HK, Foltz RL, Johnson M (1993). "Short-term effects of 2,4,5-trihydroxyamphetamine, 2,4,5-trihydroxymethamphetamine and 3,4-dihydroxymethamphetamine on central tryptophan hydroxyls activity". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 265 (2): 813–818. PMID 8496826.